—
How Pulitzer Prize-winning Paul Greenberg, one of the most respected and honored commentators in America, changed his mind about abortion and endorses now the pro-life view. Paul is the editorial page editor of the Arkansas Democrat-Gazette. This article below is from April 11, 2011.
The Doctor Who Saw What He Did
The good doctor could have stepped out of a Louis Auchincloss short story. A fashionable but conscientious professional on the Upper West Side, his ideas, like his Brooks Brothers suits, were tailored to fit in. His ideals were those of the enlightened, modern urban America of his time, which was the mid- to late 20th century. And he was always doing what he could to further them.
The doctor’s political, medical and social convictions were much what one would have expected of a New York liberal, as clear as his curriculum vitae. The son of a secular Jewish ob/gyn, he would follow his prominent father’s footsteps, graduate from McGill Medical College in Montreal, and start his practice in Manhattan. He was a quick study, whether absorbing the latest medical knowledge or political trend. Especially when it came to abortion.
Having no convictions about the sacredness of human life, he was defenseless against its growing and increasingly legal appeal. Indeed, he was soon a leader in Pro-Choice ranks.
By his own count, Bernard Nathanson, M.D., was responsible for some 75,000 abortions — without a twinge of conscience intervening. Not back then. Not when he picketed a New York City hospital in his campaign for the legalization of abortion in New York state. Preaching what he practiced, Dr. Nathanson became a tireless spokesman for NARAL, the National Association for the Repeal of Abortion Laws.
As director of the Center for Reproductive and Sexual Health in Manhattan, where he routinely performed abortions and taught others to do the same, Dr. Nathanson knew of what he spoke. And never grew tired of rationalizing it. He wasn’t destroying human life but just “an undifferentiated mass of cells.” He was performing a social service, really. He was on a humanitarian mission.
Then something happened. The something was quite specific — the newest EKG and ultrasound imagery. Always a follower of the latest scientific evidence, he couldn’t deny what he was seeing. Political theory is one thing, but facts are facts.
By 1974, soon after Roe v. Wade had opened the way to his dream of abortion-on-demand, his eyes were opened. Literally. As he put it, “There is no longer any serious doubt in my mind that human life exists within the womb from the very onset of pregnancy.” He changed his beliefs and his ways — and sides.
I can identify. When Roe v. Wade was first pronounced, I welcomed it. As a young editorial writer in Pine Bluff, Ark., I believed the court’s assurances that its ruling was not blanket permission for abortion, but a carefully crafted, limited decision applicable only in some exceptional cases. Which was all a lot of hooey, but I swallowed it, and regurgitated it in editorials.
The right to life need not be fully respected from conception on, I explained, but grew with each stage of fetal development until a full human being was formed. I went into all this in an extended debate in the columns of the Pine Bluff Commercial with a young Baptist minister in town named Mike Huckabee.
Yes, I’d been taught by Mary Warters in her biology and genetics courses at Centenary that human life was one unbroken cycle from life to death, and the code to its development was present from its microscopic origins. But I wanted to believe human rights developed differently, especially the right to life. My reasons were compassionate. Who would not want to spare mothers carrying the deformed? Why not just allow physicians to eliminate the deformity? I hadn’t yet come across Flannery O’Connor’s warning that tenderness leads to the gas chambers.
Then something happened. I noticed that the number of abortions in the country had begun to mount year by year — into the millions. Perfectly healthy babies were being aborted for socio-economic reasons. Among ethnic groups, the highest proportions of abortions were being performed on black women. (Last I checked, 37 percent of American abortions were being done on African-American women, though they make up less than 13 percent of the U.S. population.)
Eugenics was showing its true face again. And it wasn’t pretty.
Abortion was even being touted as a preventative for poverty. All you had to do, after all, was eliminate the poor. They were, in the phrase of the advanced, Darwinian thinkers of the last century, surplus population.
With a little verbal manipulation, any crime can be rationalized, even promoted. Verbicide precedes homicide. The trick is to speak of fetuses, not unborn children. So long as the victims are a faceless abstraction, anything can be done to them. Just don’t look too closely at those sonograms. We are indeed strangely and wondrously made.
By now the toll has reached some 50 million aborted babies in America since 1973. That is not an abstract theory. It is fact, and facts are stubborn things. Some carry their own imperatives with them. And so, like Dr. Nathanson, I changed my mind, and changed sides.
There is something about simple human dignity, whether the issue is civil rights in the 1960s or abortion and euthanasia today, that in the end will not be denied. And it keeps asking: Whose side are you on? Life or death?
Long before he died the other day at 84, Bernard Nathanson had chosen life. He became as ardent an advocate for life as he had once been for death. He wrote books and produced a film, “The Silent Scream,” laying out the case for the unborn, and for humanity. He would join the Catholic Church in 1996 and continue to practice medicine as chief of obstetrical services at Saint Luke’s-Roosevelt hospital in Manhattan.
“I have such heavy moral baggage to drag into the next world,” he told the Washington Times in 1996. But he also had sought to redeem himself. He could not have been expected to do other than he did in his younger years, given his appetite for fashionable ideas. He was, after all, only human. Which is no small or simple thing.
_________

223 × 373Images may be subject to copyright. Learn More
Recently I have been revisiting my correspondence in 1995 with the famous astronomer Carl Sagan who I had the privilege to correspond with in 1994, 1995 and 1996. In 1996 I had a chance to respond to his December 5, 1995letter on January 10, 1996 and I never heard back from him again since his cancer returned and he passed away later in 1996. Below is what Carl Sagan wrote to me in his December 5, 1995 letter:
Thanks for your recent letter about evolution and abortion. The correlation is hardly one to one; there are evolutionists who are anti-abortion and anti-evolutionists who are pro-abortion.You argue that God exists because otherwise we could not understand the world in our consciousness. But if you think God is necessary to understand the world, then why do you not ask the next question of where God came from? And if you say “God was always here,” why not say that the universe was always here? On abortion, my views are contained in the enclosed article (Sagan, Carl and Ann Druyan {1990}, “The Question of Abortion,” Parade Magazine, April 22.)
I was introduced to when reading a book by Francis Schaeffer called HE IS THERE AND HE IS NOT SILENT written in 1968.

Francis Schaeffer when he was a young pastor in St. Louis pictured above.

Francis Schaeffer and Adrian Rogers


(both Adrian Rogers and Francis Schaeffer mentioned Carl Sagan in their books and that prompted me to write Sagan and expose him to their views.
Carl Sagan pictured below:
_________

Francis Schaeffer
I mentioned earlier that I was blessed with the opportunity to correspond with Dr. Sagan. In his December 5, 1995 letter Dr. Sagan went on to tell me that he was enclosing his article “The Question of Abortion: A Search for Answers”by Carl Sagan and Ann Druyan. I am going to respond to several points made in that article. Here is a portion of Sagan’s article (here is a link to the whole article):

Carl Sagan and Ann Druyan pictured above
“The Question of Abortion: A Search for Answers”
by Carl Sagan and Ann Druyan
For the complete text, including illustrations, introductory quote, footnotes, and commentary on the reaction to the originally published article see Billions and Billions.
The issue had been decided years ago. The court had chosen the middle ground. You’d think the fight was over. Instead, there are mass rallies, bombings and intimidation, murders of workers at abortion clinics, arrests, intense lobbying, legislative drama, Congressional hearings, Supreme Court decisions, major political parties almost defining themselves on the issue, and clerics threatening politicians with perdition. Partisans fling accusations of hypocrisy and murder. The intent of the Constitution and the will of God are equally invoked. Doubtful arguments are trotted out as certitudes. The contending factions call on science to bolster their positions. Families are divided, husbands and wives agree not to discuss it, old friends are no longer speaking. Politicians check the latest polls to discover the dictates of their consciences. Amid all the shouting, it is hard for the adversaries to hear one another. Opinions are polarized. Minds are closed.
Is it wrong to abort a pregnancy? Always? Sometimes? Never? How do we decide? We wrote this article to understand better what the contending views are and to see if we ourselves could find a position that would satisfy us both. Is there no middle ground? We had to weigh the arguments of both sides for consistency and to pose test cases, some of which are purely hypothetical. If in some of these tests we seem to go too far, we ask the reader to be patient with us–we’re trying to stress the various positions to the breaking point to see their weaknesses and where they fail.
In contemplative moments, nearly everyone recognizes that the issue is not wholly one-sided. Many partisans of differing views, we find, feel some disquiet, some unease when confronting what’s behind the opposing arguments. (This is partly why such confrontations are avoided.) And the issue surely touches on deep questions: What are our responses to one another? Should we permit the state to intrude into the most intimate and personal aspects of our lives? Where are the boundaries of freedom? What does it mean to be human?
Of the many actual points of view, it is widely held–especially in the media, which rarely have the time or the inclination to make fine distinctions–that there are only two: “pro-choice” and “pro-life.” This is what the two principal warring camps like to call themselves, and that’s what we’ll call them here. In the simplest characterization, a pro-choicer would hold that the decision to abort a pregnancy is to be made only by the woman; the state has no right to interfere. And a pro-lifer would hold that, from the moment of conception, the embryo or fetus is alive; that this life imposes on us a moral obligation to preserve it; and that abortion is tantamount to murder. Both names–pro-choice and pro-life–were picked with an eye toward influencing those whose minds are not yet made up: Few people wish to be counted either as being against freedom of choice or as opposed to life. Indeed, freedom and life are two of our most cherished values, and here they seem to be in fundamental conflict.
Let’s consider these two absolutist positions in turn. A newborn baby is surely the same being it was just before birth. There ‘s good evidence that a late-term fetus responds to sound–including music, but especially its mother’s voice. It can suck its thumb or do a somersault. Occasionally, it generates adult brain-wave patterns. Some people claim to remember being born, or even the uterine environment. Perhaps there is thought in the womb. It’s hard to maintain that a transformation to full personhood happens abruptly at the moment of birth. Why, then, should it be murder to kill an infant the day after it was born but not the day before?
As a practical matter, this isn’t very important: Less than 1 percent of all tabulated abortions in the United States are listed in the last three months of pregnancy (and, on closer investigation, most such reports turn out to be due to miscarriage or miscalculation). But third-trimester abortions provide a test of the limits of the pro-choice point of view. Does a woman’s “innate right to control her own body” encompass the right to kill a near-term fetus who is, for all intents and purposes, identical to a newborn child?
We believe that many supporters of reproductive freedom are troubled at least occasionally by this question. But they are reluctant to raise it because it is the beginning of a slippery slope. If it is impermissible to abort a pregnancy in the ninth month, what about the eighth, seventh, sixth … ? Once we acknowledge that the state can interfere at any time in the pregnancy, doesn’t it follow that the state can interfere at all times?
Abortion and the slippery slope argument above
This conjures up the specter of predominantly male, predominantly affluent legislators telling poor women they must bear and raise alone children they cannot afford to bring up; forcing teenagers to bear children they are not emotionally prepared to deal with; saying to women who wish for a career that they must give up their dreams, stay home, and bring up babies; and, worst of all, condemning victims of rape and incest to carry and nurture the offspring of their assailants. Legislative prohibitions on abortion arouse the suspicion that their real intent is to control the independence and sexuality of women…
And yet, by consensus, all of us think it proper that there be prohibitions against, and penalties exacted for, murder. It would be a flimsy defense if the murderer pleads that this is just between him and his victim and none of the government’s business. If killing a fetus is truly killing a human being, is it not the duty of the state to prevent it? Indeed, one of the chief functions of government is to protect the weak from the strong.
If we do not oppose abortion at some stage of pregnancy, is there not a danger of dismissing an entire category of human beings as unworthy of our protection and respect? And isn’t that dismissal the hallmark of sexism, racism, nationalism, and religious fanaticism? Shouldn’t those dedicated to fighting such injustices be scrupulously careful not to embrace another?
Adrian Rogers’ sermon on animal rights refutes Sagan here
There is no right to life in any society on Earth today, nor has there been at any former time… : We raise farm animals for slaughter; destroy forests; pollute rivers and lakes until no fish can live there; kill deer and elk for sport, leopards for the pelts, and whales for fertilizer; entrap dolphins, gasping and writhing, in great tuna nets; club seal pups to death; and render a species extinct every day. All these beasts and vegetables are as alive as we. What is (allegedly) protected is not life, but human life.
Genesis 3 defines being human
And even with that protection, casual murder is an urban commonplace, and we wage “conventional” wars with tolls so terrible that we are, most of us, afraid to consider them very deeply… That protection, that right to life, eludes the 40,000 children under five who die on our planet each day from preventable starvation, dehydration, disease, and neglect.
Those who assert a “right to life” are for (at most) not just any kind of life, but for–particularly and uniquely—human life. So they too, like pro-choicers, must decide what distinguishes a human being from other animals and when, during gestation, the uniquely human qualities–whatever they are–emerge.
The Bible talks about the differences between humans and animals
Despite many claims to the contrary, life does not begin at conception: It is an unbroken chain that stretches back nearly to the origin of the Earth, 4.6 billion years ago. Nor does human life begin at conception: It is an unbroken chain dating back to the origin of our species, hundreds of thousands of years ago. Every human sperm and egg is, beyond the shadow of a doubt, alive. They are not human beings, of course. However, it could be argued that neither is a fertilized egg.
In some animals, an egg develops into a healthy adult without benefit of a sperm cell. But not, so far as we know, among humans. A sperm and an unfertilized egg jointly comprise the full genetic blueprint for a human being. Under certain circumstances, after fertilization, they can develop into a baby. But most fertilized eggs are spontaneously miscarried. Development into a baby is by no means guaranteed. Neither a sperm and egg separately, nor a fertilized egg, is more than a potential baby or a potential adult. So if a sperm and egg are as human as the fertilized egg produced by their union, and if it is murder to destroy a fertilized egg–despite the fact that it’s only potentially a baby–why isn’t it murder to destroy a sperm or an egg?
Hundreds of millions of sperm cells (top speed with tails lashing: five inches per hour) are produced in an average human ejaculation. A healthy young man can produce in a week or two enough spermatozoa to double the human population of the Earth. So is masturbation mass murder? How about nocturnal emissions or just plain sex? When the unfertilized egg is expelled each month, has someone died? Should we mourn all those spontaneous miscarriages? Many lower animals can be grown in a laboratory from a single body cell. Human cells can be cloned… In light of such cloning technology, would we be committing mass murder by destroying any potentially clonable cells? By shedding a drop of blood?
All human sperm and eggs are genetic halves of “potential” human beings. Should heroic efforts be made to save and preserve all of them, everywhere, because of this “potential”? Is failure to do so immoral or criminal? Of course, there’s a difference between taking a life and failing to save it. And there’s a big difference between the probability of survival of a sperm cell and that of a fertilized egg. But the absurdity of a corps of high-minded semen-preservers moves us to wonder whether a fertilized egg’s mere “potential” to become a baby really does make destroying it murder.
Opponents of abortion worry that, once abortion is permissible immediately after conception, no argument will restrict it at any later time in the pregnancy. Then, they fear, one day it will be permissible to murder a fetus that is unambiguously a human being. Both pro-choicers and pro-lifers (at least some of them) are pushed toward absolutist positions by parallel fears of the slippery slope.
Another slippery slope is reached by those pro-lifers who are willing to make an exception in the agonizing case of a pregnancy resulting from rape or incest. But why should the right to live depend on the circumstances of conception? If the same child were to result, can the state ordain life for the offspring of a lawful union but death for one conceived by force or coercion? How can this be just? And if exceptions are extended to such a fetus, why should they be withheld from any other fetus? This is part of the reason some pro-lifers adopt what many others consider the outrageous posture of opposing abortions under any and all circumstances–only excepting, perhaps, when the life of the mother is in danger.
By far the most common reason for abortion worldwide is birth control. So shouldn’t opponents of abortion be handing out contraceptives and teaching school children how to use them? That would be an effective way to reduce the number of abortions. Instead, the United States is far behind other nations in the development of safe and effective methods of birth control–and, in many cases, opposition to such research (and to sex education) has come from the same people who oppose abortions.continue on to Part 3
For the complete text, including illustrations, introductory quote, footnotes, and commentary on the reaction to the originally published article see Billions and Billions.
The attempt to find an ethically sound and unambiguous judgment on when, if ever, abortion is permissible has deep historical roots. Often, especially in Christian tradition, such attempts were connected with the question of when the soul enters the body–a matter not readily amenable to scientific investigation and an issue of controversy even among learned theologians. Ensoulment has been asserted to occur in the sperm before conception, at conception, at the time of “quickening” (when the mother is first able to feel the fetus stirring within her), and at birth. Or even later.
Different religions have different teachings. Among hunter-gatherers, there are usually no prohibitions against abortion, and it was common in ancient Greece and Rome. In contrast, the more severe Assyrians impaled women on stakes for attempting abortion. The Jewish Talmud teaches that the fetus is not a person and has no rights. The Old and New Testaments–rich in astonishingly detailed prohibitions on dress, diet, and permissible words–contain not a word specifically prohibiting abortion. The only passage that’s remotely relevant (Exodus 21:22) decrees that if there’s a fight and a woman bystander should accidentally be injured and made to miscarry, the assailant must pay a fine.
Neither St. Augustine nor St. Thomas Aquinas considered early-term abortion to be homicide (the latter on the grounds that the embryo doesn’t look human). This view was embraced by the Church in the Council of Vienne in 1312, and has never been repudiated. The Catholic Church’s first and long-standing collection of canon law (according to the leading historian of the Church’s teaching on abortion, John Connery, S.J.) held that abortion was homicide only after the fetus was already “formed”–roughly, the end of the first trimester.
But when sperm cells were examined in the seventeenth century by the first microscopes, they were thought to show a fully formed human being. An old idea of the homunculus was resuscitated–in which within each sperm cell was a fully formed tiny human, within whose testes were innumerable other homunculi, etc., ad infinitum. In part through this misinterpretation of scientific data, in 1869 abortion at any time for any reason became grounds for excommunication. It is surprising to most Catholics and others to discover that the date was not much earlier.
From colonial times to the nineteenth century, the choice in the United States was the woman’s until “quickening.” An abortion in the first or even second trimester was at worst a misdemeanor. Convictions were rarely sought and almost impossible to obtain, because they depended entirely on the woman’s own testimony of whether she had felt quickening, and because of the jury’s distaste for prosecuting a woman for exercising her right to choose. In 1800 there was not, so far as is known, a single statute in the United States concerning abortion. Advertisements for drugs to induce abortion could be found in virtually every newspaper and even in many church publications–although the language used was suitably euphemistic, if widely understood.
But by 1900, abortion had been banned at any time in pregnancy by every state in the Union, except when necessary to save the woman’s life. What happened to bring about so striking a reversal? Religion had little to do with it.Drastic economic and social conversions were turning this country from an agrarian to an urban-industrial society. America was in the process of changing from having one of the highest birthrates in the world to one of the lowest. Abortion certainly played a role and stimulated forces to suppress it.
One of the most significant of these forces was the medical profession. Up to the mid-nineteenth century, medicine was an uncertified, unsupervised business. Anyone could hang up a shingle and call himself (or herself) a doctor. With the rise of a new, university-educated medical elite, anxious to enhance the status and influence of physicians, the American Medical Association was formed. In its first decade, the AMA began lobbying against abortions performed by anyone except licensed physicians. New knowledge of embryology, the physicians said, had shown the fetus to be human even before quickening.
Their assault on abortion was motivated not by concern for the health of the woman but, they claimed, for the welfare of the fetus. You had to be a physician to know when abortion was morally justified, because the question depended on scientific and medical facts understood only by physicians. At the same time, women were effectively excluded from the medical schools, where such arcane knowledge could be acquired. So, as things worked out, women had almost nothing to say about terminating their own pregnancies. It was also up to the physician to decide if the pregnancy posed a threat to the woman, and it was entirely at his discretion to determine what was and was not a threat. For the rich woman, the threat might be a threat to her emotional tranquillity or even to her lifestyle. The poor woman was often forced to resort to the back alley or the coat hanger.
This was the law until the 1960s, when a coalition of individuals and organizations, the AMA now among them, sought to overturn it and to reinstate the more traditional values that were to be embodied in Roe v. Wade.continue on to Part 4
If you deliberately kill a human being, it’s called murder. If you deliberately kill a chimpanzee–biologically, our closest relative, sharing 99.6 percent of our active genes–whatever else it is, it’s not murder. To date, murder uniquely applies to killing human beings. Therefore, the question of when personhood (or, if we like, ensoulment) arises is key to the abortion debate. When does the fetus become human? When do distinct and characteristic human qualities emerge?
Section 8 Sperm journey to becoming Human
We recognize that specifying a precise moment will overlook individual differences. Therefore, if we must draw a line, it ought to be drawn conservatively–that is, on the early side. There are people who object to having to set some numerical limit, and we share their disquiet; but if there is to be a law on this matter, and it is to effect some useful compromise between the two absolutist positions, it must specify, at least roughly, a time of transition to personhood.
Every one of us began from a dot. A fertilized egg is roughly the size of the period at the end of this sentence. The momentous meeting of sperm and egg generally occurs in one of the two fallopian tubes. One cell becomes two, two become four, and so on—an exponentiation of base-2 arithmetic. By the tenth day the fertilized egg has become a kind of hollow sphere wandering off to another realm: the womb. It destroys tissue in its path. It sucks blood from capillaries. It bathes itself in maternal blood, from which it extracts oxygen and nutrients. It establishes itself as a kind of parasite on the walls of the uterus.By the third week, around the time of the first missed menstrual period, the forming embryo is about 2 millimeters long and is developing various body parts. Only at this stage does it begin to be dependent on a rudimentary placenta. It looks a little like a segmented worm.By the end of the fourth week, it’s about 5 millimeters (about 1/5 inch) long. It’s recognizable now as a vertebrate, its tube-shaped heart is beginning to beat, something like the gill arches of a fish or an amphibian become conspicuous, and there is a pronounced tail. It looks rather like a newt or a tadpole. This is the end of the first month after conception.By the fifth week, the gross divisions of the brain can be distinguished. What will later develop into eyes are apparent, and little buds appear—on their way to becoming arms and legs.By the sixth week, the embryo is 13 millimeteres (about ½ inch) long. The eyes are still on the side of the head, as in most animals, and the reptilian face has connected slits where the mouth and nose eventually will be.By the end of the seventh week, the tail is almost gone, and sexual characteristics can be discerned (although both sexes look female). The face is mammalian but somewhat piglike.By the end of the eighth week, the face resembles that of a primate but is still not quite human. Most of the human body parts are present in their essentials. Some lower brain anatomy is well-developed. The fetus shows some reflex response to delicate stimulation.By the tenth week, the face has an unmistakably human cast. It is beginning to be possible to distinguish males from females. Nails and major bone structures are not apparent until the third month.By the fourth month, you can tell the face of one fetus from that of another. Quickening is most commonly felt in the fifth month. The bronchioles of the lungs do not begin developing until approximately the sixth month, the alveoli still later.
So, if only a person can be murdered, when does the fetus attain personhood? When its face becomes distinctly human, near the end of the first trimester? When the fetus becomes responsive to stimuli–again, at the end of the first trimester? When it becomes active enough to be felt as quickening, typically in the middle of the second trimester? When the lungs have reached a stage of development sufficient that the fetus might, just conceivably, be able to breathe on its own in the outside air?
The trouble with these particular developmental milestones is not just that they’re arbitrary. More troubling is the fact that none of them involves uniquely humancharacteristics–apart from the superficial matter of facial appearance. All animals respond to stimuli and move of their own volition. Large numbers are able to breathe. But that doesn’t stop us from slaughtering them by the billions. Reflexes and motion are not what make us human.
Sagan’s conclusion based on arbitrary choice of the presence of thought by unborn baby
Other animals have advantages over us–in speed, strength, endurance, climbing or burrowing skills, camouflage, sight or smell or hearing, mastery of the air or water. Our one great advantage, the secret of our success, is thought–characteristically human thought. We are able to think things through, imagine events yet to occur, figure things out. That’s how we invented agriculture and civilization. Thought is our blessing and our curse, and it makes us who we are.
Thinking occurs, of course, in the brain–principally in the top layers of the convoluted “gray matter” called the cerebral cortex. The roughly 100 billion neurons in the brain constitute the material basis of thought. The neurons are connected to each other, and their linkups play a major role in what we experience as thinking. But large-scale linking up of neurons doesn’t begin until the 24th to 27th week of pregnancy–the sixth month.
By placing harmless electrodes on a subject’s head, scientists can measure the electrical activity produced by the network of neurons inside the skull. Different kinds of mental activity show different kinds of brain waves. But brain waves with regular patterns typical of adult human brains do not appear in the fetus until about the 30th week of pregnancy–near the beginning of the third trimester. Fetuses younger than this–however alive and active they may be–lack the necessary brain architecture. They cannot yet think.
Acquiescing in the killing of any living creature, especially one that might later become a baby, is troublesome and painful. But we’ve rejected the extremes of “always” and “never,” and this puts us–like it or not–on the slippery slope. If we are forced to choose a developmental criterion, then this is where we draw the line: when the beginning of characteristically human thinking becomes barely possible.
It is, in fact, a very conservative definition: Regular brain waves are rarely found in fetuses. More research would help… If we wanted to make the criterion still more stringent, to allow for occasional precocious fetal brain development, we might draw the line at six months. This, it so happens, is where the Supreme Court drew it in 1973–although for completely different reasons.
Its decision in the case of Roe v. Wade changed American law on abortion. It permits abortion at the request of the woman without restriction in the first trimester and, with some restrictions intended to protect her health, in the second trimester. It allows states to forbid abortion in the third trimester, except when there’s a serious threat to the life or health of the woman. In the 1989 Webster decision, the Supreme Court declined explicitly to overturn Roe v. Wade but in effect invited the 50 state legislatures to decide for themselves.
What was the reasoning in Roe v. Wade? There was no legal weight given to what happens to the children once they are born, or to the family. Instead, a woman’s right to reproductive freedom is protected, the court ruled, by constitutional guarantees of privacy. But that right is not unqualified. The woman’s guarantee of privacy and the fetus’s right to life must be weighed–and when the court did the weighing’ priority was given to privacy in the first trimester and to life in the third. The transition was decided not from any of the considerations we have been dealing with so far…–not when “ensoulment” occurs, not when the fetus takes on sufficient human characteristics to be protected by laws against murder. Instead, the criterion adopted was whether the fetus could live outside the mother. This is called “viability” and depends in part on the ability to breathe. The lungs are simply not developed, and the fetus cannot breathe–no matter how advanced an artificial lung it might be placed in—until about the 24th week, near the start of the sixth month. This is why Roe v. Wade permits the states to prohibit abortions in the last trimester. It’s a very pragmatic criterion.
If the fetus at a certain stage of gestation would be viable outside the womb, the argument goes, then the right of the fetus to life overrides the right of the woman to privacy. But just what does “viable” mean? Even a full-term newborn is not viable without a great deal of care and love. There was a time before incubators, only a few decades ago, when babies in their seventh month were unlikely to be viable. Would aborting in the seventh month have been permissible then? After the invention of incubators, did aborting pregnancies in the seventh month suddenly become immoral? What happens if, in the future, a new technology develops so that an artificial womb can sustain a fetus even before the sixth month by delivering oxygen and nutrients through the blood–as the mother does through the placenta and into the fetal blood system? We grant that this technology is unlikely to be developed soon or become available to many. But if it were available, does it then become immoral to abort earlier than the sixth month, when previously it was moral? A morality that depends on, and changes with, technology is a fragile morality; for some, it is also an unacceptable morality.
And why, exactly, should breathing (or kidney function, or the ability to resist disease) justify legal protection? If a fetus can be shown to think and feel but not be able to breathe, would it be all right to kill it? Do we value breathing more than thinking and feeling? Viability arguments cannot, it seems to us, coherently determine when abortions are permissible. Some other criterion is needed. Again, we offer for consideration the earliest onset of human thinking as that criterion.
Since, on average, fetal thinking occurs even later than fetal lung development, we find Roe v. Wade to be a good and prudent decision addressing a complex and difficult issue. With prohibitions on abortion in the last trimester–except in cases of grave medical necessity–it strikes a fair balance between the conflicting claims of freedom and life.What do you think? What have others said about Carl Sagan’s thoughts on
END OF SAGAN’S ARTICLE
Carl Sagan, in full Carl Edward Sagan, (born November 9, 1934, Brooklyn, New York, U.S.—died December 20, 1996, Seattle, Washington), American astronomer and science writer. A popular and influential figure in the United States, he was controversial in scientific, political, and religious circles for his views on extraterrestrial intelligence, nuclear weapons, and religion. Sagan wrote the article “life” for the 1970 printing of the 14th edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica (1929–73).
Sagan attended the University of Chicago, where he earned a bachelor’s and a master’s degree in physics in 1955 and 1956, respectively, and a doctorate in astronomy and astrophysics in 1960. From 1960 to 1962 he was a fellow in astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley, and from 1962 to 1968 he worked at Harvard University and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. His early work focused on the physical conditions of the planets, especially the atmospheres of Venus and Jupiter. During that time he became interested in the possibility of lifebeyond Earth and the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI), a controversial research field he did much to advance. For example, building on earlier work by American chemists Stanley Miller and Harold Urey, he demonstrated that amino acids and nucleic acids—the building blocks of life—could be produced by exposing a mixture of simple chemicals to ultraviolet radiation. Some scientists criticized Sagan’s work, arguing that it was unreasonable to use resources for SETI, a fantasy project that was almost certainly doomed to failure.
On November 21, 2014 I received a letter from Nobel Laureate Harry Kroto and it said:
…Please click on this URL http://vimeo.com/26991975
and you will hear what far smarter people than I have to say on this matter. I agree with them.
Harry Kroto

I have attempted to respond to all of Dr. Kroto’s friends arguments and I have posted my responses one per week for over a year now. Here are some of my earlier posts:
Arif Ahmed, Haroon Ahmed, Jim Al-Khalili, Sir David Attenborough, Mark Balaguer, Horace Barlow, Michael Bate, Sir Patrick Bateson, Simon Blackburn, Colin Blakemore, Ned Block, Pascal Boyer, Patricia Churchland, Aaron Ciechanover, Noam Chomsky, Brian Cox, Partha Dasgupta, Alan Dershowitz, Frank Drake, Hubert Dreyfus, John Dunn, Bart Ehrman, Mark Elvin, Richard Ernst, Stephan Feuchtwang, Robert Foley, David Friend, Riccardo Giacconi, Ivar Giaever , Roy Glauber, Rebecca Goldstein, David J. Gross, Brian Greene, Susan Greenfield, Stephen F Gudeman, Alan Guth, Jonathan Haidt, Theodor W. Hänsch, Brian Harrison, Stephen Hawking, Hermann Hauser, Robert Hinde, Roald Hoffmann, Bruce Hood, Gerard ‘t Hooft, Caroline Humphrey, Nicholas Humphrey, Herbert Huppert, Gareth Stedman Jones, Steve Jones, Shelly Kagan, Michio Kaku, Stuart Kauffman, Masatoshi Koshiba, Lawrence Krauss, Harry Kroto, George Lakoff, Rodolfo Llinas, Elizabeth Loftus, Alan Macfarlane, Dan McKenzie, Mahzarin Banaji, Peter Millican, Marvin Minsky, Leonard Mlodinow, P.Z.Myers, Yujin Nagasawa, Alva Noe, Douglas Osheroff, David Parkin, Jonathan Parry, Roger Penrose, Saul Perlmutter, Herman Philipse, Carolyn Porco, Robert M. Price, VS Ramachandran, Lisa Randall, Lord Martin Rees, Colin Renfrew, Alison Richard, C.J. van Rijsbergen, Oliver Sacks, John Searle, Marcus du Sautoy, Simon Schaffer, J. L. Schellenberg, Lee Silver, Peter Singer, Walter Sinnott-Armstrong, Ronald de Sousa, Victor Stenger, John Sulston, Barry Supple, Leonard Susskind, Raymond Tallis, Max Tegmark, Neil deGrasse Tyson, Martinus J. G. Veltman, Craig Venter, .Alexander Vilenkin, Sir John Walker, James D. Watson, Frank Wilczek, Steven Weinberg, and Lewis Wolpert,
In the 1st video below in the 45th clip in this series are his words and my response is below them.
50 Renowned Academics Speaking About God (Part 1)
Another 50 Renowned Academics Speaking About God (Part 2
A Further 50 Renowned Academics Speaking About God (Part 3)
–
CARL SAGAN interview with Charlie Rose:
“…faith is belief in the absence of evidence. To believe in the absence of evidence, in my opinion, is a mistake. The idea is to hold belief until there is compelling evidence. If the Universe does not comply with our previous propositions, then we have to change…Religion deals with history poetry, great literature, ethics, morals, compassion…where religion gets into trouble is when it pretends to know something about science,”
I would respond that there is evidence that Christianity is true. The Bible has fulfilled prophecy in it, and 53 historical notable people in the Bible have been confirmed through archaeological evidence! Also there is compelling evidence that the Bible contains sound medical principles that clearly predate their more recent discovery by thousands of years
Related posts:
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 52 THE BEATLES (Part D, There is evidence that the Beatles may have been exposed to Francis Schaeffer!!!) (Feature on artist Anna Margaret Rose Freeman )
______________ George Harrison Swears & Insults Paul and Yoko Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds- The Beatles The Beatles: I have dedicated several posts to this series on the Beatles and I don’t know when this series will end because Francis Schaeffer spent a lot of time listening to the Beatles and talking […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 51 THE BEATLES (Part C, List of those on cover of Stg.Pepper’s ) (Feature on artist Raqib Shaw )
The Beatles in a press conference after their Return from the USA Uploaded on Nov 29, 2010 The Beatles in a press conference after their Return from the USA. The Beatles: I have dedicated several posts to this series on the Beatles and I don’t know when this series will end because Francis […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 50 THE BEATLES (Part B, The Psychedelic Music of the Beatles) (Feature on artist Peter Blake )
__________________ Beatles 1966 Last interview I have dedicated several posts to this series on the Beatles and I don’t know when this series will end because Francis Schaeffer spent a lot of time listening to the Beatles and talking and writing about them and their impact on the culture of the 1960’s. In this […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 49 THE BEATLES (Part A, The Meaning of Stg. Pepper’s Cover) (Feature on artist Mika Tajima)
_______________ The Beatles documentary || A Long and Winding Road || Episode 5 (This video discusses Stg. Pepper’s creation I have dedicated several posts to this series on the Beatles and I don’t know when this series will end because Francis Schaeffer spent a lot of time listening to the Beatles and talking and writing about […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE PART 48 “BLOW UP” by Michelangelo Antonioni makes Philosophic Statement (Feature on artist Nancy Holt)
_______________ Francis Schaeffer pictured below: _____________________ I have included the 27 minute episode THE AGE OF NONREASON by Francis Schaeffer. In that video Schaeffer noted, ” Sergeant Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band…for a time it became the rallying cry for young people throughout the world. It expressed the essence of their lives, thoughts and their feelings.” How Should […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 47 Woody Allen and Professor Levy and the death of “Optimistic Humanism” from the movie CRIMES AND MISDEMEANORS Plus Charles Darwin’s comments too!!! (Feature on artist Rodney Graham)
Crimes and Misdemeanors: A Discussion: Part 1 ___________________________________ Today I will answer the simple question: IS IT POSSIBLE TO BE AN OPTIMISTIC SECULAR HUMANIST THAT DOES NOT BELIEVE IN GOD OR AN AFTERLIFE? This question has been around for a long time and you can go back to the 19th century and read this same […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE PART 46 Friedrich Nietzsche (Featured artist is Thomas Schütte)
____________________________________ Francis Schaeffer pictured below: __________ Francis Schaeffer has written extensively on art and culture spanning the last 2000years and here are some posts I have done on this subject before : Francis Schaeffer’s “How should we then live?” Video and outline of episode 10 “Final Choices” , episode 9 “The Age of Personal Peace and Affluence”, episode 8 […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 45 Woody Allen “Reason is Dead” (Feature on artists Allora & Calzadilla )
Love and Death [Woody Allen] – What if there is no God? [PL] ___________ _______________ How Should We then Live Episode 7 small (Age of Nonreason) #02 How Should We Then Live? (Promo Clip) Dr. Francis Schaeffer 10 Worldview and Truth Two Minute Warning: How Then Should We Live?: Francis Schaeffer at 100 Francis Schaeffer […]
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 44 The Book of Genesis (Featured artist is Trey McCarley )
___________________________________ Francis Schaeffer pictured below: ____________________________ Francis Schaeffer “BASIS FOR HUMAN DIGNITY” Whatever…HTTHR Dr. Francis schaeffer – The flow of Materialism(from Part 4 of Whatever happened to human race?) Dr. Francis Schaeffer – The Biblical flow of Truth & History (intro) Francis Schaeffer – The Biblical Flow of History & Truth (1) Dr. Francis Schaeffer […]
__
__












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():gifv():focal(404x450:406x452)/king-charles-johnny-cash-092022-b14901fbe3f1422ab7af6a7e4788caa1.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(764x259:766x261):format(webp)/queen-funeral-king-charles-close-up-091922-de7afe0bff6642658cd1c5f70ef6272c.jpg)















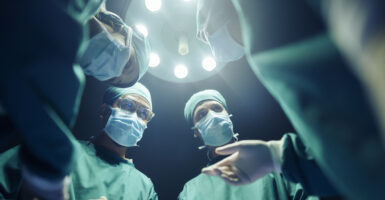



 True discernment has suffered a horrible setback in the past few decades because reason itself has been under attack within the church. As Francis Schaeffer warned nearly thirty years ago in The God Who Is There, the church is following the irrationality of secular philosophy. Consequently, reckless faith has overrun the evangelical community. Many are discarding doctrine in favor of personal experience. Others say they are willing to disregard crucial biblical distinctives in order to achieve external unity among all professing Christians. True Christianity marked by intelligent, biblical faith seems to be declining even among the most conservative evangelicals.THE ABANDONMENT OF OBJECTIVE TRUTHThe visible church in our generation has become astonishingly tolerant of aberrant teaching and outlandish ideas—and frighteningly intolerant of sound teaching. The popular evangelical conception of “truth” has become almost completely subjective. Truth is viewed as fluid, always relative, never absolute. To suggest that any objective criterion might be used to distinguish truth from error is to be egregiously out of step with the spirit of the age. In some circles, Scripture itself has been ruled out as a reliable test of truth. After all, the Bible can be interpreted in so many different ways—who can say which interpretation is right? And many believe there is truth beyond the Bible.All this relativity has had disastrous effects on the typical Christian’s ability to discern truth from error, right from wrong, good from evil. The plainest teachings of the Bible are being questioned among people who declare themselves believers in the Bible. For example, some Christians are no longer certain whether homosexuality should be classed as a sin. Others argue that the feminist agenda is compatible with biblical Christianity. “Christian” television, radio, books, and magazines serve up a preposterous smorgasbord of ideas from the merely capricious to the downright dangerous—and the average Christian is woefully ill-equipped to sort out the lies from the truth.Even to suggest that a sorting between lies and truth is necessary is viewed by many as perilously intolerant. There is a notion abroad that any dispute over doctrine is inherently evil. Concern for orthodoxy is regarded as incompatible with Christian unity. Doctrine itself is labeled divisive and those who make doctrine an issue are branded uncharitable. No one is permitted to criticize anyone else’s beliefs, no matter how unbiblical those beliefs seem to be. A recent article in Christianity Today exemplifies the trend. The article, titled “Hunting for Heresy,” profiled two well-known Christian leaders who had “come under withering attack for controversial writings.”1One is a popular speaker on the college lecture circuit and a bestselling author. He wrote a book in which he encouraged homosexuals to establish permanent live-together relationships (albeit celibate ones). He suggests the evangelical community suffers from “homophobia.” He is convinced that permanent living arrangements between homosexuals are the only alternative to loneliness for people he believes are “born with a homosexual orientation.” This man’s wife has published an article in a homosexual magazine in which she enthusiastically affirms” monogamous sexual relationships between homosexuals. The speaker-author says he has a “very, very strong” disagreement with his wife’s approval of homosexual sex, but his own view seems to allow homosexuals to engage in other kinds of physical intimacy short of actual intercourse.The other Christian leader profiled in the Christianity Today article is a woman who, with her husband, is a featured speaker for a popular, nationally-syndicated radio and television ministry. Their ministry is not a weird offshoot from some fringe cult, but an established, well-respected mainstay from the evangelical heartland. She also serves as chairperson of one of the largest evangelical student organizations in the world. This woman has written a book in which she chronicles some rather peculiar spiritual experiences. She dedicates the book to her male alter ego, an imaginary person named “Eddie Bishop” who romances her in her dreams. This woman says she also has visions of “the Christ child that is within” her. He appears to her as a drooling, emaciated, barefoot “idiot child” in a torn undershirt—”its head totally bald and lolled to one side.” The woman has engaged the services of a Catholic nun who serves as her “spiritual director,” helping to interpret her dreams and fantasies. The book mingles mysticism, Jungian psychology, out-of-body experiences, feminist ideas, subjective religious experience, and this woman’s romantic fantasies into an extraordinary amalgam. The book is frankly so bizarre that it is disturbing to read.The remarkable thing about the Christianity Today article is that the story was not written to expose the aberrant ideas being taught by these two leading evangelicals. Instead, what the magazine’s editors deemed newsworthy was the fact that these people were under attack for their views.In the world of modern evangelicalism, it is allowable to advocate the most unconventional, unbiblical doctrines—as long as you afford everyone else the same privilege. About the only thing that is taboo nowadays is the intolerance of those who dare to point out others’ errors. Anyone today who is bold enough to suggest that someone else’s ideas or doctrines are unsound or unbiblical is dismissed at once as contentious, divisive, unloving, or unchristian. It is all right toespouse any view you wish, but it is not all right to criticize another person’s views—no matter how patently unbiblical those views may be.When tolerance is valued over truth, the cause of truth always suffers. Church history shows this to be so. Only when the people of God have mounted a hardy defense of truth and sound doctrine has the church flourished and grown strong. The Reformation, the Puritan era, and the Great Awakenings are all examples of this. The times of decline in the history of the church have always been marked by an undue emphasis on tolerance—which leads inevitably to carelessness, worldliness, doctrinal compromise, and great confusion in the church.ADRIFT ON A SEA OF SUBJECTIVITYThat the church would lose her moorings in this particular age, however, poses greater dangers than ever. For in the past hundred years or so, the world has changed in a dramatic and very frightening way. People no longer look at truth the way they used to. In fact, we live under a prevailing philosophy that has become hostile to the very idea of absolute truth.From the beginning of recorded history until late last century, virtually all human philosophy assumed the necessity of absolute truth. Truth was universally understood as that which is true, not false; factual, not erroneous; correct, not incorrect; moral, not immoral; just, not unjust; right, not wrong. Practically all philosophers since the time of Plato assumed the objectivity of truth. Philosophy itself was a quest for the highest understanding of truth. Such a pursuit was presumed to be possible, even necessary, because truth was understood to be the same for every person. This did not mean that everyone agreed what truth was, of course. But virtually all agreed that whatever was true was true for everyone.That all changed in the nineteenth century with the birth of existentialism. Existentialism defies precise definition, but it includes the concept that the highest truth is subjective (having its source in the individual’s mind) rather than objective (something that actually exists outside the individual). Existentialism elevates individual experience and personal choice, minimizing or ruling out absolute standards of truth, goodness, morality, and such things. We might accurately characterize existentialism as the abandonment of objectivity. Existentialism is inherently anti-intellectual, against reason, irrational.Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard first used the term “existential.” Kierkegaard’s life and philosophy revolved around his experiences with Christianity. Christian ideas and biblical terminology reverberate in many of his writings. He wrote much about faith and certainly regarded himself as a Christian. Many of his ideas began as a legitimate reaction against the stale formalism of the Danish Lutheran state church. He was rightly offended at the barren ritualism of the church, properly outraged that people who had no love for God called themselves Christians just because they happened to be born in a “Christian” nation.But in his reaction against the lifeless state church, Kierkegaard set up a false antithesis. He decided that objectivity and truth were incompatible. To counter the passionless ritualism and lifeless doctrinal formulas he saw in Danish Lutheranism, Kierkegaard devised an approach to religion that was pure passion, altogether subjective. Faith, he suggested, means the rejection of reason and the exaltation of feeling and personal experience. It was Kierkegaard who coined the expression “leap of faith.” Faith to him was an irrational experience, above all a personal choice. He recorded these words in his journal on August 1, 1835: “The thing is to find a truth which is true for me, to find the idea for which I can live and die.”2Clearly, Kierkegaard had already rejected as inherently worthless the belief that truth is objective. His journal continues with these words:What would be the use of discovering so-called objective truth …. What good would it do me if truth stood before me, cold and naked, not caring whether I recognized her or not, and producing in me a shudder of fear rather than a trusting devotion? … I am left standing like a man who has rented a house and gathered all the furniture and household things together, but has not yet found the beloved with whom to share the joys and sorrows of his life…. It is this divine side of man, his inward action, which means everything—not a mass of [objective] information.3Having repudiated the objectivity of truth, Kierkegaard was left longing for an existential experience, which he believed would bring him a sense of personal fulfillment. He stood on the precipice, preparing to make his leap of faith. Ultimately, the idea he chose to live and die for was Christianity, but it was a characteristically subjective brand of Christianity that he embraced.Though Kierkegaard was virtually unknown during his lifetime, his writings have endured and have deeply influenced all subsequent philosophy. His idea of “truth that is true for me” infiltrated popular thought and set the tone for our generations radical rejection of all objective standards.Kierkegaard knew how to make irrationalism sound profound. “God does not exist; He is eternal,” he wrote. He believed Christianity was full of “existential paradoxes,” which he regarded as actual contradictions, proof that truth is irrational.Using the example of Abraham’s willingness to sacrifice Isaac (Gen. 22:1-19), Kierkegaard suggested that God called Abraham to violate moral law in slaying his son. For Kierkegaard, Abraham’s willingness to “suspend” his ethical convictions epitomized the leap of faith that is demanded of everyone. Kierkegaard believed the incident proved that “the single individual [Abraham] is higher than the universal [moral law].”4 Building on that conclusion, the Danish philosopher offered this observation: “Abraham represents faith…. He acts by virtue of the absurd, for it is precisely [by virtue of] the absurd that he as the single individual is higher than the universal.”5 “[I] cannot understand Abraham,” Kierkegaard declared, “even though in a certain demented sense I admire him more than all others.”6It is not difficult to see how such thinking thrusts all truth into the realm of pure subjectivity—even to the point of absurdity or dementia. Everything becomes relative. Absolutes dematerialize. The difference between truth and nonsense becomes meaningless. All that matters is personal experience.And one person’s experience is as valid as another’s—even if everyone’s experiences lead to contradictory conceptions of truth. “Truth that is true for me” might be different from someone else’s truth. In fact, our beliefs might be obviously contradictory, yet another person’s “truth” in no way invalidates mine. Because “truth”is authenticated by personal experience, its only relevance is for the individual who makes the leap of faith. That is existentialism.Existentialism caught on in a big way in secular philosophy. Friedrich Nietzsche, for example, also rejected reason and emphasized the will of the individual. Nietzsche probably knew nothing of Kierkegaard’s works, but their ideas paralleled at the key points. Unlike Kierkegaard, however, Nietzsche never made the leap of faith to Christianity. Instead, he leapt to the conclusion that God is dead. The truth that was “true for him,” it seems, turned out to be the opposite of the truth Kierkegaard chose. But their epistemology (the way they arrived at their ideas) was exactly the same.Later existentialists, such as Martin Heidegger and Jean-Paul Sartre, refined Kierkegaard’s ideas while following the atheism of Nietzsche. Heidegger and Sartre both believed that reason is futile and life basically meaningless. Those ideas have been a powerful force in twentieth-century thought. As the world continues to grow more atheistic, more secular, and more irrational, it helps to understand that it is being propelled in that direction by strong existentialist influences.EXISTENTIALISM INVADES THE CHURCH But don’t get the idea that existentialism’s influence is limited to the secular world. From the moment Kierkegaard wedded existentialist ideas with Christianity, neo-orthodox theology was the inevitable outcome.Neo-orthodoxy is the term used to identify an existentialist variety of Christianity. Because it denies the essential objective basis of truth—the absolute truth and authority of Scripture—neo-orthodoxy must be understood as pseudo-Christianity. Its heyday came in the middle of the twentieth century with the writings of Karl Barth, Emil Brunner, Paul Tillich, and Reinhold Niebuhr. Those men echoed the language and the thinking of Kierkegaard, speaking of the primacy of “personal authenticity,” while downplaying or denying the significance of objective truth. Barth, the father of neo-orthodoxy, explicitly acknowledged his debt to Kierkegaard.7Neo-orthodoxy’s attitude toward Scripture is a microcosm of the entire existentialist philosophy: the Bible itself is not objectively the Word of God, but it becomes the Word of God when it speaks to me individually. In neo-orthodoxy, that same subjectivism is imposed on all the doctrines of historic Christianity. Familiar terms are used, but are redefined or employed in a way that is purposely vague—not to convey objective meaning, but to communicate a subjective symbolism. After all, any “truth” theological terms convey is unique to the person who exercises faith. What the Bible means becomes unimportant. What it means to me is the relevant issue. All of this resoundingly echoes Kierkegaard’s concept of “truth that is true for me.”Thus while neo-orthodox theologians often sound as if they are affirming traditional beliefs, their actual system differs radically from the historic understanding of the Christian faith. By denying the objectivity of truth, they relegate all theology to the realm of subjective relativism. It is a theology perfectly suited for the age in which we live.And that is precisely why it is so deadly.Francis Schaeffer’s 1968 work The God Who Is There included a perceptive analysis of Kierkegaard’s influence on modern thought and modern theology.8 Schaeffer named the boundary between rationality and irrationality “the line of despair.” He noted that existentialism pushed secular thought below the line of despair sometime in the nineteenth century. Religious neo-orthodoxy was simply a johnny-come-lately response of theologians who were jumping on the existentialist bandwagon, following secular art, music, and general culture: “Neo-orthodoxy gave no new answer. What existential philosophy had already said in secular language, it now said in theological language…. [With the advent of neo-orthodoxy,] theology too has gone below the line of despair.”9Schaeffer went on to analyze how neo-orthodoxy ultimately gives way to radical mysticism:Karl Barth opened the door to the existentialistic leap in theology… He has been followed by many more, men like Reinhold Niebuhr, Paul Tillich, Bishop John Robinson, Alan Richardson and all the new theologians. They may differ in details, but their struggle is still the same—it is the struggle of modern man who has given up [rationality]. As far as the theologians are concerned … their new system is not open to verification, it must simply be believed.10Such a system, Schaeffer points out, has no integrity. Those who espouse it cannot live with the repercussions of their own illogic. “In practice a man cannot totally reject [rationality], however much his system leads him to it, unless he experiences … some form of mental breakdown.” Thus people have been forced to an even deeper level of despair: “a level of mysticism with nothing there.”11MYSTICISM: IRRATIONALITY GONE TO SEEDMysticism is the idea that spiritual reality is found by looking inward. Mysticism is perfectly suited for religious existentialism; indeed, it is its inevitable consequence. The mystic disdains rational understanding and seeks truth instead through the feelings, the imagination, personal visions, inner voices, private illumination, or other purely subjective means. Objective truth becomes practically superfluous. Mystical experiences are therefore self-authenticating; that is, they are not subject to any form of objective verification. They are unique to the person who experiences them. Since they do not arise from or depend upon any rational process, they are invulnerable to any refutation by rational means.Arthur L. Johnson writes,The experience convinces the mystic in such a way, and to such a degree, that lie simply cannot doubt its value and the correctness of what he believes it “says.”…In its crudest form this position says that believing something to be so makes it so. The idea is that ultimate reality is purely mental; therefore one is able to create whatever reality one wishes. Thus the mystic “creates” truth through his experience. In a less extreme form, the view seems to be that there are “alternate realities,” one as real as another, and that these “break in upon” the mystic in his experiences. Whatever form is taken, the criterion of truth is again a purely private and subjective experience that provides no means of verification and no safeguard against error. Nevertheless, it is seen by the mystic as being above question by others.The practical result of all this is that it is nearly impossible to reason with any convinced mystic. Such people are generally beyond the reach of reason.12Mysticism is therefore antithetical to discernment. It is an extreme form of reckless faith.Mysticism is the great melting pot into which neo-orthodoxy, the charismatic movement, anti-intellectual evangelicals, and even some segments of Roman Catholicism have been synthesized. It has produced movements like the Third Wave (a neo-charismatic movement with excessive emphasis on signs, wonders, and personal prophecies); Renovaré (an organization that blends teachings from monasticism, ancient Catholic mysticism, Eastern religion, and other mystical traditions); the spiritual warfare movement (which seeks to engage demonic powers in direct confrontation); and the modern prophecy movement (which encourages believers to seek private, extrabiblical revelation directly ftom God). The influx of mysticism has also opened evangelicalism to New-Age concepts like subliminal thought- control, inner healing, communication with angels, channeling, dream analysis, positive confession, and a host of other therapies andpractices coming directly from occult and Eastern religions. The face of evangelicalism has changed so dramatically in the past twenty years that what is called evangelicalism today is beginning to resemble what used to be called neo-orthodoxy. If anything, some segments of contemporary evangelicalism are even more subjective in their approach to truth than neo-orthodoxy ever was.It could be argued that evangelicalism never successfully resisted neo-orthodoxy. Twenty years ago evangelicals took a heroic stand against neo-orthodox influences on the issue of biblical inerrancy. But whatever victory was gained in that battle is now being sacrificed on the altar of mysticism. Mysticism renders biblical inerrancy irrelevant. After all, if the highest truth is subjective and comes from within us, then it doesn’t ultimately matter if the specifics of Scripture are true or not. If the content of faith is not the real issue, what does it really matter if the Bible has errors or not?In other words, neo-orthodoxy attacked the objective inspiration of Scripture. Evangelical mysticism attacks the objective interpretation of Scripture. The practical effect is the same. By embracing existential relativism, evangelicals are forfeiting the very riches they fought so hard to protect. If we can gain meaningful guidance from characters who appear in our fantasies, why should we bother ourselves with what the Bible says? If we are going to disregard or even reject the biblical verdict against homosexuality, what difference does it make if the historical and factual matter revealed in Scripture is accurate or inaccurate? If personal prophecies, visions, dreams, and angelic beings are available to give us up-to-the-minute spiritual direction—”fresh revelation” as it is often called—who cares if Scripture is without error in the whole or in the parts?Mysticism further nullifies Scripture by pointing people away from the sure Word of God as the only reliable object of faith. Warning of the dangers of mysticism, Schaeffer wrote,Probably the best way to describe this concept of modern theology is to say that it is faith in faith, rather than faith directed to an object which is actually there…. A modern man cannot talk about the object of his faith, only about the faith itself. So he can discuss the existence of his faith and its “size” as it exists against all reason, but that is all. Modern man’s faith turns inward…. Faith is introverted, because it has no certain object … it is rationally not open to discussion. This position, I would suggest, is actually a greater despair and darkness than the position of those modern men who commit suicide.“13The faith of mysticism is an illusion. “Truth that is true for me” is irrelevant to anyone else, because it lacks any objective basis. Ultimately, therefore, existential faith is impotent to lift anyone above the level of despair. All it can do is seek more experiences and more feelings. Multitudes are trapped in the desperate cycle of feeding off one experience while zealously seeking the next. Such people have no real concept of truth; they just believe. Theirs is a reckless faith.MEANWHILE, AT THE OTHER END OF THE SPECTRUM…Mysticism, however, is not the only form of reckless faith that threatens the contemporary church. A new movement has been gaining strength lately. Evangelicals are leaving the fold and moving into Eastern Orthodoxy, Roman Catholicism, and liturgical high-church Protestantism. Rejecting the ever-changing subjectivism of a free- wheeling existential Protestantism, they seek a religion with historical roots. Turned off by the shallow silliness that has overrun the evangelical movement, they desire a more magisterial approach. Perhaps sensing the dangers of a religion that points people inward, they choose instead a religion that emphasizes external ceremonies and dogmatic hierarchical authority.I listened to the taped testimony of one of these converts to Roman Catholicism, a former Protestant minister. He said he had graduated with highest honors from a leading Protestant seminary. He told his audience that as a student he was rabidly anti-Catholic and fully committed to Protestant Reformed doctrine (although he refuted this himself by admitting he had already rejected the crucial doctrine of justification by faith). After college he began to read Roman Catholic writings and found himself drawn to Catholic theology and liturgy. He described his initial resistance to the doctrines of purgatory, the perpetual virginity of Mary, transubstantiation, and prayers to Mary and the saints. All of those doctrines are easily disproved by the Bible.14 But this man—acknowledging that he could find no warrant anywhere in Scripture for praying to Mary—nevertheless completely changed his outlook on such matters after he tried praying the rosary and received an answer to a very specific prayer. He concluded that it must have been Mary who answered his prayer and immediately began praying regularly to her. Ultimately, he decided the Bible alone was not a sufficient rule of faith for believers, and he put his faith in papal authority and church tradition.That man’s leap of faith may not have been of the existential variety, but it was a blind leap nonetheless. He chose the other extreme of reckless faith, the kind that makes extrabiblical religious tradition the object of one’s faith.This kind of faith is reckless because it subjugates the written Word of God to oral tradition, church authority, or some other human criterion. It is an uncritical trust in an earthly religious authority—the pope, tradition, a self-styled prophet like David Koresh, or whatever. Such faith rarely jettisons Scripture altogether—but by forcing God’s Word into the mold of religious tradition, it invalidates the Word of God and renders it of no effect (cf. Matt. 15:6).The man whose taped testimony I heard is now an apologist for the Roman Catholic Church. He speaks to Catholic congregations and tells them how to counter biblical arguments against Catholicism. At the end of his testimony tape, he deals briefly with the official Catholic attitude toward Scripture. He is eager to assure his listeners that the modern Roman Catholic Church has no objection if Catholic people want to read Scripture for themselves. Even personal Bible study is all right, he says—but then hastens to add that it is not necessary to go overboard. “A verse or two a day is enough.” This man, a seminary graduate, surely should be aware that a comment like that seriously understates the importance of the written Word of God. We are commanded to meditate on Scripture day and night (Josh. 1:8; Ps. 1:2). We are to let it fill our hearts at all times (Deut. 6:6-9). We must study it diligently and handle it rightly (2 Tim. 2:15). The Bible alone is able to give us the wisdom that leads to salvation, then adequately equip us for every good work (2 Tim. 3:15-17).Discernment depends on a knowledge of Scripture. Those who are content to listen gullibly to some voice of human authority rather than hearing God’s Word and letting it speak for itself cannot be discerning. Theirs is a reckless, irrational faith.We identified the inward-looking extreme of reckless faith as mysticism. We could call this other variety rote tradition. In Isaiah 29:13, that is precisely how God Himself characterized it: “This people their lip service, but draw near with their words and honor Me with their lip service, but they remove their hearts far from Me, and their reverence for Me consists of tradition learned by rote” (emphasis added).Scripture has nothing but condemnation for rote tradition. Barren religious ritual, sacerdotal formalism, or liturgy out of a book are not the same as worship. Real worship, like faith, must engage the mind. Jesus said, “The true worshipers … worship the Father in spirit and truth; for such people the Father seeks to be His worshipers” (John 4:23).Did you realize that rote tradition was the very error for which Jesus condemned the Pharisees? He told them,“Rightly did Isaiah prophesy of you hypocrites, as it is written, ‘This people honors Me with their lips, but their heart is far away from Me. But in vain do they worship Me. teaching as doctrines the precepts of men.’ Neglecting the commandment of God, you hold to the tradition of men.”He was also saying to them, “You nicely set aside the commandment of God in order to keep your tradition” (Mark 7:6-9).Rote tradition is not unlike mysticism in that it also bypasses the mind. Paul said this of the Jews who were so absorbed in their empty religious traditions:I bear them witness that they have a zeal for God, but not in accordance with knowledge. For not knowing about God’s righteousness, and seeking to establish their own, they did not subject themselves to the righteousness of God. For Christ is the end of the law for righteousness to everyone who believes (Rom. 10:2-4).Their problem was not a lack of zeal. It was not that they were short on enthusiasm, emotionally flat, or slothful about religious observances. The issue was that the zeal they displayed was rote tradition, “not in accordance with knowledge.” They were not sufficiently discerning, and therefore their faith itself was deficient.Paul is specific in stating that their ignorance lay in trying to establish their own righteousness rather than submitting to the righteousness of God. This passage comes at the culmination of Paul’s doctrinal discussion in Romans. In context it is very clear that he was talking about the doctrine ofjustification by faith. He had thoroughly expounded this subject beginning in chapter 3. He said we are “justified as a gift by His grace through the redemption which is in Christ Jesus” (3:24). Justification is “by faith apart from works of the Law” (v.28). “God reckons righteousness apart from works” (Rom. 4:6).But instead of seeking the perfect righteousness of Christ, which God reckons to those who believe, the unbelieving Jews had set out to try to establish a righteousness of their own through works. That is where rote tradition always leads. It is a religion of works. Thus the ritualistic, unbelieving Pharisees are an exact parallel to Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and most forms of ritual-laden Protestantism. All of them deny justification by faith.If the Pharisees or their followers had used the Scriptures as their standard of truth rather than rabbinical tradition, they would have known that God justifies sinners by faith. Repeatedly, Jesus said things to them like “Did you never read in the Scriptures . . . ?” (Matt. 21:42); “You are mistaken, not understanding the Scriptures, or the power of God” (22:29); and, “Are you the teacher of Israel, and do not understand these things?” (John 3:10). What He continually chided them for was their ignorance of the Scriptures. They had set rote tradition in place of the written Word of God (Matt. 15:6), and they were condemned for it.Contrast the way Luke commended the Bereans for their noblemindedness: “For they received the word [the New Testament gospel from the apostles] with great eagerness, examining the Scriptures [the Old Testament books] daily, to see whether these things were so” (Acts 17:1 1). What made the Bereans worthy of commendation? Their eagerness to be discerning. They rightly refused to blindly accept anyone’s teaching (even that of the apostles) without clear warrant from God’s Word.Spiritual discernment is, I believe, the only antidote to the existentialism of our age. Until’Christians regain the will to test everything by the rule of Scripture, reject what is false, and hold fast to what is true, the church will struggle and falter, and our testimony to a world in sin will be impaired.But if the church will rise up and stand for the truth of God’s Word against all the lies of this evil world, then we will begin to see the power of truth that sets people free (John 8:32).Endnotes1. John W. Kennedy, “Hunting for Heresy,” Christianity Today (16 May 1994).2. Robert Bretall, cd., A Kierkegaard Anthology (Princeton, N. J.: Princeton University Press, 1946), 5 (emphasis in original).3. Ibid.4. Søren Kierkegaard, Fear and Trembling, Howard V. Hong and Edna H. Hong, trans. (Princeton, N. J.: Princeton University Press, 1983), 55.5. Ibid.6. Ibid., 57.7. Karl Barth, The Epistle to the Romans, Edwyn C. Hoskyns, trans. (London: Oxford University Press, 1933). Barth cites Kierkegaard repeatedly in this, one of his earliest works.8. Francis Schaeffer, The God Who Is There, in The Complete Works of Francis A. Schaeffer, Volume I (Wheaton, Ill.: Crossway Books, 1982).9. Ibid., 53.10. Ibid., 55.11. Ibid., 58.12. Arthur L. Johnson, Faith Misguided: Exposing the Dangers of Mysticism (Chicago: Moody Press, 1988), 31-32.13. Schaeffer, 64-65, emphasis added.14. Purgatory: Luke 23:42-43 and 2 Cor. 5:8 indicate that believers go immediately to be with Christ at death. Perpetual Virginity of Mary: Matt. 1:25 states that Joseph kept Mary a virgin only until Jesus’ birth, and John 2:12 and Acts 1:14 reveal that Jesus had brothers. Transubstantiation: Heb. 7:27 and 10:12 teach that Christ made one sacrifice for sins forever; there is no need for the daily sacrifice of the Mass. Prayers to Mary and the saints: prayers, adoration, and spiritual veneration offered to anyone but God is expressly forbidden by the first commandment and elsewhere throughout Scripture (Ex. 20:3; Matt. 4:10; Acts 10:25-26; Rev. 19:10; Rev. 22:8-9).Excerpt from Reckless Faith: When the Church Loses Its Will to Discern, © 1994 by John MacArthur.We do pray this article has blessed you in some way. Our prayer is that you will use this message to better understand what is happening in our churches today.Blessings,
True discernment has suffered a horrible setback in the past few decades because reason itself has been under attack within the church. As Francis Schaeffer warned nearly thirty years ago in The God Who Is There, the church is following the irrationality of secular philosophy. Consequently, reckless faith has overrun the evangelical community. Many are discarding doctrine in favor of personal experience. Others say they are willing to disregard crucial biblical distinctives in order to achieve external unity among all professing Christians. True Christianity marked by intelligent, biblical faith seems to be declining even among the most conservative evangelicals.THE ABANDONMENT OF OBJECTIVE TRUTHThe visible church in our generation has become astonishingly tolerant of aberrant teaching and outlandish ideas—and frighteningly intolerant of sound teaching. The popular evangelical conception of “truth” has become almost completely subjective. Truth is viewed as fluid, always relative, never absolute. To suggest that any objective criterion might be used to distinguish truth from error is to be egregiously out of step with the spirit of the age. In some circles, Scripture itself has been ruled out as a reliable test of truth. After all, the Bible can be interpreted in so many different ways—who can say which interpretation is right? And many believe there is truth beyond the Bible.All this relativity has had disastrous effects on the typical Christian’s ability to discern truth from error, right from wrong, good from evil. The plainest teachings of the Bible are being questioned among people who declare themselves believers in the Bible. For example, some Christians are no longer certain whether homosexuality should be classed as a sin. Others argue that the feminist agenda is compatible with biblical Christianity. “Christian” television, radio, books, and magazines serve up a preposterous smorgasbord of ideas from the merely capricious to the downright dangerous—and the average Christian is woefully ill-equipped to sort out the lies from the truth.Even to suggest that a sorting between lies and truth is necessary is viewed by many as perilously intolerant. There is a notion abroad that any dispute over doctrine is inherently evil. Concern for orthodoxy is regarded as incompatible with Christian unity. Doctrine itself is labeled divisive and those who make doctrine an issue are branded uncharitable. No one is permitted to criticize anyone else’s beliefs, no matter how unbiblical those beliefs seem to be. A recent article in Christianity Today exemplifies the trend. The article, titled “Hunting for Heresy,” profiled two well-known Christian leaders who had “come under withering attack for controversial writings.”1One is a popular speaker on the college lecture circuit and a bestselling author. He wrote a book in which he encouraged homosexuals to establish permanent live-together relationships (albeit celibate ones). He suggests the evangelical community suffers from “homophobia.” He is convinced that permanent living arrangements between homosexuals are the only alternative to loneliness for people he believes are “born with a homosexual orientation.” This man’s wife has published an article in a homosexual magazine in which she enthusiastically affirms” monogamous sexual relationships between homosexuals. The speaker-author says he has a “very, very strong” disagreement with his wife’s approval of homosexual sex, but his own view seems to allow homosexuals to engage in other kinds of physical intimacy short of actual intercourse.The other Christian leader profiled in the Christianity Today article is a woman who, with her husband, is a featured speaker for a popular, nationally-syndicated radio and television ministry. Their ministry is not a weird offshoot from some fringe cult, but an established, well-respected mainstay from the evangelical heartland. She also serves as chairperson of one of the largest evangelical student organizations in the world. This woman has written a book in which she chronicles some rather peculiar spiritual experiences. She dedicates the book to her male alter ego, an imaginary person named “Eddie Bishop” who romances her in her dreams. This woman says she also has visions of “the Christ child that is within” her. He appears to her as a drooling, emaciated, barefoot “idiot child” in a torn undershirt—”its head totally bald and lolled to one side.” The woman has engaged the services of a Catholic nun who serves as her “spiritual director,” helping to interpret her dreams and fantasies. The book mingles mysticism, Jungian psychology, out-of-body experiences, feminist ideas, subjective religious experience, and this woman’s romantic fantasies into an extraordinary amalgam. The book is frankly so bizarre that it is disturbing to read.The remarkable thing about the Christianity Today article is that the story was not written to expose the aberrant ideas being taught by these two leading evangelicals. Instead, what the magazine’s editors deemed newsworthy was the fact that these people were under attack for their views.In the world of modern evangelicalism, it is allowable to advocate the most unconventional, unbiblical doctrines—as long as you afford everyone else the same privilege. About the only thing that is taboo nowadays is the intolerance of those who dare to point out others’ errors. Anyone today who is bold enough to suggest that someone else’s ideas or doctrines are unsound or unbiblical is dismissed at once as contentious, divisive, unloving, or unchristian. It is all right toespouse any view you wish, but it is not all right to criticize another person’s views—no matter how patently unbiblical those views may be.When tolerance is valued over truth, the cause of truth always suffers. Church history shows this to be so. Only when the people of God have mounted a hardy defense of truth and sound doctrine has the church flourished and grown strong. The Reformation, the Puritan era, and the Great Awakenings are all examples of this. The times of decline in the history of the church have always been marked by an undue emphasis on tolerance—which leads inevitably to carelessness, worldliness, doctrinal compromise, and great confusion in the church.ADRIFT ON A SEA OF SUBJECTIVITYThat the church would lose her moorings in this particular age, however, poses greater dangers than ever. For in the past hundred years or so, the world has changed in a dramatic and very frightening way. People no longer look at truth the way they used to. In fact, we live under a prevailing philosophy that has become hostile to the very idea of absolute truth.From the beginning of recorded history until late last century, virtually all human philosophy assumed the necessity of absolute truth. Truth was universally understood as that which is true, not false; factual, not erroneous; correct, not incorrect; moral, not immoral; just, not unjust; right, not wrong. Practically all philosophers since the time of Plato assumed the objectivity of truth. Philosophy itself was a quest for the highest understanding of truth. Such a pursuit was presumed to be possible, even necessary, because truth was understood to be the same for every person. This did not mean that everyone agreed what truth was, of course. But virtually all agreed that whatever was true was true for everyone.That all changed in the nineteenth century with the birth of existentialism. Existentialism defies precise definition, but it includes the concept that the highest truth is subjective (having its source in the individual’s mind) rather than objective (something that actually exists outside the individual). Existentialism elevates individual experience and personal choice, minimizing or ruling out absolute standards of truth, goodness, morality, and such things. We might accurately characterize existentialism as the abandonment of objectivity. Existentialism is inherently anti-intellectual, against reason, irrational.Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard first used the term “existential.” Kierkegaard’s life and philosophy revolved around his experiences with Christianity. Christian ideas and biblical terminology reverberate in many of his writings. He wrote much about faith and certainly regarded himself as a Christian. Many of his ideas began as a legitimate reaction against the stale formalism of the Danish Lutheran state church. He was rightly offended at the barren ritualism of the church, properly outraged that people who had no love for God called themselves Christians just because they happened to be born in a “Christian” nation.But in his reaction against the lifeless state church, Kierkegaard set up a false antithesis. He decided that objectivity and truth were incompatible. To counter the passionless ritualism and lifeless doctrinal formulas he saw in Danish Lutheranism, Kierkegaard devised an approach to religion that was pure passion, altogether subjective. Faith, he suggested, means the rejection of reason and the exaltation of feeling and personal experience. It was Kierkegaard who coined the expression “leap of faith.” Faith to him was an irrational experience, above all a personal choice. He recorded these words in his journal on August 1, 1835: “The thing is to find a truth which is true for me, to find the idea for which I can live and die.”2Clearly, Kierkegaard had already rejected as inherently worthless the belief that truth is objective. His journal continues with these words:What would be the use of discovering so-called objective truth …. What good would it do me if truth stood before me, cold and naked, not caring whether I recognized her or not, and producing in me a shudder of fear rather than a trusting devotion? … I am left standing like a man who has rented a house and gathered all the furniture and household things together, but has not yet found the beloved with whom to share the joys and sorrows of his life…. It is this divine side of man, his inward action, which means everything—not a mass of [objective] information.3Having repudiated the objectivity of truth, Kierkegaard was left longing for an existential experience, which he believed would bring him a sense of personal fulfillment. He stood on the precipice, preparing to make his leap of faith. Ultimately, the idea he chose to live and die for was Christianity, but it was a characteristically subjective brand of Christianity that he embraced.Though Kierkegaard was virtually unknown during his lifetime, his writings have endured and have deeply influenced all subsequent philosophy. His idea of “truth that is true for me” infiltrated popular thought and set the tone for our generations radical rejection of all objective standards.Kierkegaard knew how to make irrationalism sound profound. “God does not exist; He is eternal,” he wrote. He believed Christianity was full of “existential paradoxes,” which he regarded as actual contradictions, proof that truth is irrational.Using the example of Abraham’s willingness to sacrifice Isaac (Gen. 22:1-19), Kierkegaard suggested that God called Abraham to violate moral law in slaying his son. For Kierkegaard, Abraham’s willingness to “suspend” his ethical convictions epitomized the leap of faith that is demanded of everyone. Kierkegaard believed the incident proved that “the single individual [Abraham] is higher than the universal [moral law].”4 Building on that conclusion, the Danish philosopher offered this observation: “Abraham represents faith…. He acts by virtue of the absurd, for it is precisely [by virtue of] the absurd that he as the single individual is higher than the universal.”5 “[I] cannot understand Abraham,” Kierkegaard declared, “even though in a certain demented sense I admire him more than all others.”6It is not difficult to see how such thinking thrusts all truth into the realm of pure subjectivity—even to the point of absurdity or dementia. Everything becomes relative. Absolutes dematerialize. The difference between truth and nonsense becomes meaningless. All that matters is personal experience.And one person’s experience is as valid as another’s—even if everyone’s experiences lead to contradictory conceptions of truth. “Truth that is true for me” might be different from someone else’s truth. In fact, our beliefs might be obviously contradictory, yet another person’s “truth” in no way invalidates mine. Because “truth”is authenticated by personal experience, its only relevance is for the individual who makes the leap of faith. That is existentialism.Existentialism caught on in a big way in secular philosophy. Friedrich Nietzsche, for example, also rejected reason and emphasized the will of the individual. Nietzsche probably knew nothing of Kierkegaard’s works, but their ideas paralleled at the key points. Unlike Kierkegaard, however, Nietzsche never made the leap of faith to Christianity. Instead, he leapt to the conclusion that God is dead. The truth that was “true for him,” it seems, turned out to be the opposite of the truth Kierkegaard chose. But their epistemology (the way they arrived at their ideas) was exactly the same.Later existentialists, such as Martin Heidegger and Jean-Paul Sartre, refined Kierkegaard’s ideas while following the atheism of Nietzsche. Heidegger and Sartre both believed that reason is futile and life basically meaningless. Those ideas have been a powerful force in twentieth-century thought. As the world continues to grow more atheistic, more secular, and more irrational, it helps to understand that it is being propelled in that direction by strong existentialist influences.EXISTENTIALISM INVADES THE CHURCH But don’t get the idea that existentialism’s influence is limited to the secular world. From the moment Kierkegaard wedded existentialist ideas with Christianity, neo-orthodox theology was the inevitable outcome.Neo-orthodoxy is the term used to identify an existentialist variety of Christianity. Because it denies the essential objective basis of truth—the absolute truth and authority of Scripture—neo-orthodoxy must be understood as pseudo-Christianity. Its heyday came in the middle of the twentieth century with the writings of Karl Barth, Emil Brunner, Paul Tillich, and Reinhold Niebuhr. Those men echoed the language and the thinking of Kierkegaard, speaking of the primacy of “personal authenticity,” while downplaying or denying the significance of objective truth. Barth, the father of neo-orthodoxy, explicitly acknowledged his debt to Kierkegaard.7Neo-orthodoxy’s attitude toward Scripture is a microcosm of the entire existentialist philosophy: the Bible itself is not objectively the Word of God, but it becomes the Word of God when it speaks to me individually. In neo-orthodoxy, that same subjectivism is imposed on all the doctrines of historic Christianity. Familiar terms are used, but are redefined or employed in a way that is purposely vague—not to convey objective meaning, but to communicate a subjective symbolism. After all, any “truth” theological terms convey is unique to the person who exercises faith. What the Bible means becomes unimportant. What it means to me is the relevant issue. All of this resoundingly echoes Kierkegaard’s concept of “truth that is true for me.”Thus while neo-orthodox theologians often sound as if they are affirming traditional beliefs, their actual system differs radically from the historic understanding of the Christian faith. By denying the objectivity of truth, they relegate all theology to the realm of subjective relativism. It is a theology perfectly suited for the age in which we live.And that is precisely why it is so deadly.Francis Schaeffer’s 1968 work The God Who Is There included a perceptive analysis of Kierkegaard’s influence on modern thought and modern theology.8 Schaeffer named the boundary between rationality and irrationality “the line of despair.” He noted that existentialism pushed secular thought below the line of despair sometime in the nineteenth century. Religious neo-orthodoxy was simply a johnny-come-lately response of theologians who were jumping on the existentialist bandwagon, following secular art, music, and general culture: “Neo-orthodoxy gave no new answer. What existential philosophy had already said in secular language, it now said in theological language…. [With the advent of neo-orthodoxy,] theology too has gone below the line of despair.”9Schaeffer went on to analyze how neo-orthodoxy ultimately gives way to radical mysticism:Karl Barth opened the door to the existentialistic leap in theology… He has been followed by many more, men like Reinhold Niebuhr, Paul Tillich, Bishop John Robinson, Alan Richardson and all the new theologians. They may differ in details, but their struggle is still the same—it is the struggle of modern man who has given up [rationality]. As far as the theologians are concerned … their new system is not open to verification, it must simply be believed.10Such a system, Schaeffer points out, has no integrity. Those who espouse it cannot live with the repercussions of their own illogic. “In practice a man cannot totally reject [rationality], however much his system leads him to it, unless he experiences … some form of mental breakdown.” Thus people have been forced to an even deeper level of despair: “a level of mysticism with nothing there.”11MYSTICISM: IRRATIONALITY GONE TO SEEDMysticism is the idea that spiritual reality is found by looking inward. Mysticism is perfectly suited for religious existentialism; indeed, it is its inevitable consequence. The mystic disdains rational understanding and seeks truth instead through the feelings, the imagination, personal visions, inner voices, private illumination, or other purely subjective means. Objective truth becomes practically superfluous. Mystical experiences are therefore self-authenticating; that is, they are not subject to any form of objective verification. They are unique to the person who experiences them. Since they do not arise from or depend upon any rational process, they are invulnerable to any refutation by rational means.Arthur L. Johnson writes,The experience convinces the mystic in such a way, and to such a degree, that lie simply cannot doubt its value and the correctness of what he believes it “says.”…In its crudest form this position says that believing something to be so makes it so. The idea is that ultimate reality is purely mental; therefore one is able to create whatever reality one wishes. Thus the mystic “creates” truth through his experience. In a less extreme form, the view seems to be that there are “alternate realities,” one as real as another, and that these “break in upon” the mystic in his experiences. Whatever form is taken, the criterion of truth is again a purely private and subjective experience that provides no means of verification and no safeguard against error. Nevertheless, it is seen by the mystic as being above question by others.The practical result of all this is that it is nearly impossible to reason with any convinced mystic. Such people are generally beyond the reach of reason.12Mysticism is therefore antithetical to discernment. It is an extreme form of reckless faith.Mysticism is the great melting pot into which neo-orthodoxy, the charismatic movement, anti-intellectual evangelicals, and even some segments of Roman Catholicism have been synthesized. It has produced movements like the Third Wave (a neo-charismatic movement with excessive emphasis on signs, wonders, and personal prophecies); Renovaré (an organization that blends teachings from monasticism, ancient Catholic mysticism, Eastern religion, and other mystical traditions); the spiritual warfare movement (which seeks to engage demonic powers in direct confrontation); and the modern prophecy movement (which encourages believers to seek private, extrabiblical revelation directly ftom God). The influx of mysticism has also opened evangelicalism to New-Age concepts like subliminal thought- control, inner healing, communication with angels, channeling, dream analysis, positive confession, and a host of other therapies andpractices coming directly from occult and Eastern religions. The face of evangelicalism has changed so dramatically in the past twenty years that what is called evangelicalism today is beginning to resemble what used to be called neo-orthodoxy. If anything, some segments of contemporary evangelicalism are even more subjective in their approach to truth than neo-orthodoxy ever was.It could be argued that evangelicalism never successfully resisted neo-orthodoxy. Twenty years ago evangelicals took a heroic stand against neo-orthodox influences on the issue of biblical inerrancy. But whatever victory was gained in that battle is now being sacrificed on the altar of mysticism. Mysticism renders biblical inerrancy irrelevant. After all, if the highest truth is subjective and comes from within us, then it doesn’t ultimately matter if the specifics of Scripture are true or not. If the content of faith is not the real issue, what does it really matter if the Bible has errors or not?In other words, neo-orthodoxy attacked the objective inspiration of Scripture. Evangelical mysticism attacks the objective interpretation of Scripture. The practical effect is the same. By embracing existential relativism, evangelicals are forfeiting the very riches they fought so hard to protect. If we can gain meaningful guidance from characters who appear in our fantasies, why should we bother ourselves with what the Bible says? If we are going to disregard or even reject the biblical verdict against homosexuality, what difference does it make if the historical and factual matter revealed in Scripture is accurate or inaccurate? If personal prophecies, visions, dreams, and angelic beings are available to give us up-to-the-minute spiritual direction—”fresh revelation” as it is often called—who cares if Scripture is without error in the whole or in the parts?Mysticism further nullifies Scripture by pointing people away from the sure Word of God as the only reliable object of faith. Warning of the dangers of mysticism, Schaeffer wrote,Probably the best way to describe this concept of modern theology is to say that it is faith in faith, rather than faith directed to an object which is actually there…. A modern man cannot talk about the object of his faith, only about the faith itself. So he can discuss the existence of his faith and its “size” as it exists against all reason, but that is all. Modern man’s faith turns inward…. Faith is introverted, because it has no certain object … it is rationally not open to discussion. This position, I would suggest, is actually a greater despair and darkness than the position of those modern men who commit suicide.“13The faith of mysticism is an illusion. “Truth that is true for me” is irrelevant to anyone else, because it lacks any objective basis. Ultimately, therefore, existential faith is impotent to lift anyone above the level of despair. All it can do is seek more experiences and more feelings. Multitudes are trapped in the desperate cycle of feeding off one experience while zealously seeking the next. Such people have no real concept of truth; they just believe. Theirs is a reckless faith.MEANWHILE, AT THE OTHER END OF THE SPECTRUM…Mysticism, however, is not the only form of reckless faith that threatens the contemporary church. A new movement has been gaining strength lately. Evangelicals are leaving the fold and moving into Eastern Orthodoxy, Roman Catholicism, and liturgical high-church Protestantism. Rejecting the ever-changing subjectivism of a free- wheeling existential Protestantism, they seek a religion with historical roots. Turned off by the shallow silliness that has overrun the evangelical movement, they desire a more magisterial approach. Perhaps sensing the dangers of a religion that points people inward, they choose instead a religion that emphasizes external ceremonies and dogmatic hierarchical authority.I listened to the taped testimony of one of these converts to Roman Catholicism, a former Protestant minister. He said he had graduated with highest honors from a leading Protestant seminary. He told his audience that as a student he was rabidly anti-Catholic and fully committed to Protestant Reformed doctrine (although he refuted this himself by admitting he had already rejected the crucial doctrine of justification by faith). After college he began to read Roman Catholic writings and found himself drawn to Catholic theology and liturgy. He described his initial resistance to the doctrines of purgatory, the perpetual virginity of Mary, transubstantiation, and prayers to Mary and the saints. All of those doctrines are easily disproved by the Bible.14 But this man—acknowledging that he could find no warrant anywhere in Scripture for praying to Mary—nevertheless completely changed his outlook on such matters after he tried praying the rosary and received an answer to a very specific prayer. He concluded that it must have been Mary who answered his prayer and immediately began praying regularly to her. Ultimately, he decided the Bible alone was not a sufficient rule of faith for believers, and he put his faith in papal authority and church tradition.That man’s leap of faith may not have been of the existential variety, but it was a blind leap nonetheless. He chose the other extreme of reckless faith, the kind that makes extrabiblical religious tradition the object of one’s faith.This kind of faith is reckless because it subjugates the written Word of God to oral tradition, church authority, or some other human criterion. It is an uncritical trust in an earthly religious authority—the pope, tradition, a self-styled prophet like David Koresh, or whatever. Such faith rarely jettisons Scripture altogether—but by forcing God’s Word into the mold of religious tradition, it invalidates the Word of God and renders it of no effect (cf. Matt. 15:6).The man whose taped testimony I heard is now an apologist for the Roman Catholic Church. He speaks to Catholic congregations and tells them how to counter biblical arguments against Catholicism. At the end of his testimony tape, he deals briefly with the official Catholic attitude toward Scripture. He is eager to assure his listeners that the modern Roman Catholic Church has no objection if Catholic people want to read Scripture for themselves. Even personal Bible study is all right, he says—but then hastens to add that it is not necessary to go overboard. “A verse or two a day is enough.” This man, a seminary graduate, surely should be aware that a comment like that seriously understates the importance of the written Word of God. We are commanded to meditate on Scripture day and night (Josh. 1:8; Ps. 1:2). We are to let it fill our hearts at all times (Deut. 6:6-9). We must study it diligently and handle it rightly (2 Tim. 2:15). The Bible alone is able to give us the wisdom that leads to salvation, then adequately equip us for every good work (2 Tim. 3:15-17).Discernment depends on a knowledge of Scripture. Those who are content to listen gullibly to some voice of human authority rather than hearing God’s Word and letting it speak for itself cannot be discerning. Theirs is a reckless, irrational faith.We identified the inward-looking extreme of reckless faith as mysticism. We could call this other variety rote tradition. In Isaiah 29:13, that is precisely how God Himself characterized it: “This people their lip service, but draw near with their words and honor Me with their lip service, but they remove their hearts far from Me, and their reverence for Me consists of tradition learned by rote” (emphasis added).Scripture has nothing but condemnation for rote tradition. Barren religious ritual, sacerdotal formalism, or liturgy out of a book are not the same as worship. Real worship, like faith, must engage the mind. Jesus said, “The true worshipers … worship the Father in spirit and truth; for such people the Father seeks to be His worshipers” (John 4:23).Did you realize that rote tradition was the very error for which Jesus condemned the Pharisees? He told them,“Rightly did Isaiah prophesy of you hypocrites, as it is written, ‘This people honors Me with their lips, but their heart is far away from Me. But in vain do they worship Me. teaching as doctrines the precepts of men.’ Neglecting the commandment of God, you hold to the tradition of men.”He was also saying to them, “You nicely set aside the commandment of God in order to keep your tradition” (Mark 7:6-9).Rote tradition is not unlike mysticism in that it also bypasses the mind. Paul said this of the Jews who were so absorbed in their empty religious traditions:I bear them witness that they have a zeal for God, but not in accordance with knowledge. For not knowing about God’s righteousness, and seeking to establish their own, they did not subject themselves to the righteousness of God. For Christ is the end of the law for righteousness to everyone who believes (Rom. 10:2-4).Their problem was not a lack of zeal. It was not that they were short on enthusiasm, emotionally flat, or slothful about religious observances. The issue was that the zeal they displayed was rote tradition, “not in accordance with knowledge.” They were not sufficiently discerning, and therefore their faith itself was deficient.Paul is specific in stating that their ignorance lay in trying to establish their own righteousness rather than submitting to the righteousness of God. This passage comes at the culmination of Paul’s doctrinal discussion in Romans. In context it is very clear that he was talking about the doctrine ofjustification by faith. He had thoroughly expounded this subject beginning in chapter 3. He said we are “justified as a gift by His grace through the redemption which is in Christ Jesus” (3:24). Justification is “by faith apart from works of the Law” (v.28). “God reckons righteousness apart from works” (Rom. 4:6).But instead of seeking the perfect righteousness of Christ, which God reckons to those who believe, the unbelieving Jews had set out to try to establish a righteousness of their own through works. That is where rote tradition always leads. It is a religion of works. Thus the ritualistic, unbelieving Pharisees are an exact parallel to Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and most forms of ritual-laden Protestantism. All of them deny justification by faith.If the Pharisees or their followers had used the Scriptures as their standard of truth rather than rabbinical tradition, they would have known that God justifies sinners by faith. Repeatedly, Jesus said things to them like “Did you never read in the Scriptures . . . ?” (Matt. 21:42); “You are mistaken, not understanding the Scriptures, or the power of God” (22:29); and, “Are you the teacher of Israel, and do not understand these things?” (John 3:10). What He continually chided them for was their ignorance of the Scriptures. They had set rote tradition in place of the written Word of God (Matt. 15:6), and they were condemned for it.Contrast the way Luke commended the Bereans for their noblemindedness: “For they received the word [the New Testament gospel from the apostles] with great eagerness, examining the Scriptures [the Old Testament books] daily, to see whether these things were so” (Acts 17:1 1). What made the Bereans worthy of commendation? Their eagerness to be discerning. They rightly refused to blindly accept anyone’s teaching (even that of the apostles) without clear warrant from God’s Word.Spiritual discernment is, I believe, the only antidote to the existentialism of our age. Until’Christians regain the will to test everything by the rule of Scripture, reject what is false, and hold fast to what is true, the church will struggle and falter, and our testimony to a world in sin will be impaired.But if the church will rise up and stand for the truth of God’s Word against all the lies of this evil world, then we will begin to see the power of truth that sets people free (John 8:32).Endnotes1. John W. Kennedy, “Hunting for Heresy,” Christianity Today (16 May 1994).2. Robert Bretall, cd., A Kierkegaard Anthology (Princeton, N. J.: Princeton University Press, 1946), 5 (emphasis in original).3. Ibid.4. Søren Kierkegaard, Fear and Trembling, Howard V. Hong and Edna H. Hong, trans. (Princeton, N. J.: Princeton University Press, 1983), 55.5. Ibid.6. Ibid., 57.7. Karl Barth, The Epistle to the Romans, Edwyn C. Hoskyns, trans. (London: Oxford University Press, 1933). Barth cites Kierkegaard repeatedly in this, one of his earliest works.8. Francis Schaeffer, The God Who Is There, in The Complete Works of Francis A. Schaeffer, Volume I (Wheaton, Ill.: Crossway Books, 1982).9. Ibid., 53.10. Ibid., 55.11. Ibid., 58.12. Arthur L. Johnson, Faith Misguided: Exposing the Dangers of Mysticism (Chicago: Moody Press, 1988), 31-32.13. Schaeffer, 64-65, emphasis added.14. Purgatory: Luke 23:42-43 and 2 Cor. 5:8 indicate that believers go immediately to be with Christ at death. Perpetual Virginity of Mary: Matt. 1:25 states that Joseph kept Mary a virgin only until Jesus’ birth, and John 2:12 and Acts 1:14 reveal that Jesus had brothers. Transubstantiation: Heb. 7:27 and 10:12 teach that Christ made one sacrifice for sins forever; there is no need for the daily sacrifice of the Mass. Prayers to Mary and the saints: prayers, adoration, and spiritual veneration offered to anyone but God is expressly forbidden by the first commandment and elsewhere throughout Scripture (Ex. 20:3; Matt. 4:10; Acts 10:25-26; Rev. 19:10; Rev. 22:8-9).Excerpt from Reckless Faith: When the Church Loses Its Will to Discern, © 1994 by John MacArthur.We do pray this article has blessed you in some way. Our prayer is that you will use this message to better understand what is happening in our churches today.Blessings,










