Is God a Delusion? – William Lane Craig vs Lewis Wolpert
Professor Craig debated Professor Wolpert at Central Hall, Westminster, Feb. 28, 2007, with John Humphrys in the chair. Professor Wolpert is Professor of Biology as Applied to Medicine at University College, London and is well known for his atheistic beliefs.
We welcome your comments in the Reasonable Faith forums:
http://www.reasonablefaith.org/forums
_________
Dr. Lewis Wolpert pictured below:
_________________
On November 21, 2014 I received a letter from Nobel Laureate Harry Kroto and it said:
…Please click on this URL http://vimeo.com/26991975
and you will hear what far smarter people than I have to say on this matter. I agree with them.
Harry Kroto
__________________________
There are 3 videos in this series and they have statements by 150 academics and scientists and I hope to respond to all of them. Wikipedia notes Lewis Wolpert CBE FRS FRSL FMedSci (born 19 October 1929) is South African-born British developmental biologist, author, and broadcaster.
Wolpert was born into a South African Jewish family.[1] He was educated at the University of Witwatersrand (BSc), at Imperial College London, and at King’s College London (PhD). As of 2010 he holds the position of Emeritus Professor of Biology as applied to Medicine in the Department of Anatomy and developmental biology at University College London….In addition to his scientific and research publications, he has written about his own experience of clinical depression in Malignant Sadness: The Anatomy of Depression (1999). He presented three television programmes based on the book and entitled A Living Hell on BBC2. He was made a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1980 and awarded the CBE in 1990. He became a Fellow of the Royal Society of Literature in 1999 and one of the first Fellows of the Academy of Medical Sciences in 1998. He serves as a Vice-President of the British Humanist Association.
_____________________________
In the second video below in the 64th clip in this series are his words and my response is below them.
50 Renowned Academics Speaking About God (Part 1)
Another 50 Renowned Academics Speaking About God (Part 2)
A Further 50 Renowned Academics Speaking About God (Part 3)
I grew up at Bellevue Baptist Church under the leadership of our pastor Adrian Rogers and I read many books by the Evangelical Philosopher Francis Schaeffer and have had the opportunity to contact many of the evolutionists or humanistic academics that they have mentioned in their works. Many of these scholars have taken the time to respond back to me in the last 20 years and some of the names included are Ernest Mayr (1904-2005), George Wald (1906-1997), Carl Sagan (1934-1996), Robert Shapiro (1935-2011), Nicolaas Bloembergen (1920-), Brian Charlesworth (1945-), Francisco J. Ayala (1934-) Elliott Sober (1948-), Kevin Padian (1951-), Matt Cartmill (1943-) , Milton Fingerman (1928-), John J. Shea (1969-), , Michael A. Crawford (1938-), Paul Kurtz (1925-2012), Sol Gordon (1923-2008), Albert Ellis (1913-2007), Barbara Marie Tabler (1915-1996), Renate Vambery (1916-2005), Archie J. Bahm (1907-1996), Aron S “Gil” Martin ( 1910-1997), Matthew I. Spetter (1921-2012), H. J. Eysenck (1916-1997), Robert L. Erdmann (1929-2006), Mary Morain (1911-1999), Lloyd Morain (1917-2010), Warren Allen Smith (1921-), Bette Chambers (1930-), Gordon Stein (1941-1996) , Milton Friedman (1912-2006), John Hospers (1918-2011), Michael Martin (1932-).Harry Kroto (1939-), Marty E. Martin (1928-), Richard Rubenstein (1924-), James Terry McCollum (1936-), Edward O. WIlson (1929-), Lewis Wolpert (1929), Gerald Holton (1922-), and Ray T. Cragun (1976-).
_____________
Lewis Wolpert Quote:
I am not against people being religious. I think it helps you a great deal. I am against religion when it interferes in the lives of other people…If you believe for example that the fertilized egg is really a human being which some people in your religious organizations believe then I am very hostile to you because it is nonsense and this is one of my subjects developmental biology or if you are against contraception for religious reason then therefore AIDS can become more common. So I am not against people having a belief in God. I do believe that believe is false. Whatever arguments I give you I have no delusion that I will persuade you to change your minds.
______________________
Let me give three examples and then I want to move on to what Dr. Wolpert’s real issue is. First, I will give the example of a former abortionist and an atheist at the time who gave up his lucrative business because of the advance of medical technology. Second, I will tell the story of a personal friend of mine who is a pro-life atheist named Dr. Kevin Henke. Third, I will list the evidence from 4 non christians who are experts in the area of genetics.
Abortionist Bernard Nathanson said it was the technology of the ultra-sound that caused him to shut down his abortion clinics since he released that these unborn babies were feeling pain. At the time Dr. Nathanson was a confirmed atheist. In his book he noted, “I worked hard to make abortion legal, affordable, and available on demand. In 1968, I was one of the three founders of the National Abortion Rights Action League. I ran the largest abortion clinic …and oversaw tens of thousands of abortions. I have performed thousands myself.” p. 5.
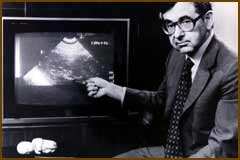
(Former Abortionist Bernard Nathanson pictured above.)
The Hand of God-Selected Quotes from Bernard N. Nathanson, M.D.,
“Embryos are Dependent Creatures. So are fetuses. So are we all dependent; on the kindness or tolerance of others, and on various biological and medical devices…Surely, dependency is not a measure of moral standing…” p. 128. The Silent Scream. By 1984, however, I had begun to ask myself more questions about abortion: What actually goes on in an abortion? I had done many, but abortion is a blind procedure. The doctor does not see what he is doing. He puts an instrument into a uterus and he turns on a motor, and a suction machines goes on and something is vacuumed out; it ends up as a little pile of meat in a gauze bag, I wanted to know what happened, so in 1984 I said to a friend of mine, who was doing fifteen or maybe twenty abortions a day, “Look, do me a favor, Jay. Next Saturday, when you are doing all these abortions, put an ultrasound device on the mother and tape it for me.”He did, and when he looked at the tapes with me in an editing studio, he was so affected that he never did another abortion…The tapes were amazing…weren’t of very good quality… and began to show it pro-life gatherings… p. 141Nathanson then recounts Silent Scream, the movie:
I was speaking at pro-life meetings around the country on weekends, and the response to the tape was so intense and dramatic that finally I was approached by a man named Don Smith, who wanted to make my tape into a film. I agreed that it would be a good idea. That is how The Silent Scream, which generated so much furor, came to be made. We showed it for the first time in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, on January 3, 1985. The reaction was instantaneous. Everybody was up in arms because The Silent Scream represented an enormous threat to the abortion forces and because it escalated the war (it’s not really a debate–we don’t debate each other; we scream at one another). For the first time, we had the technology and they had nothing. p.141 Emphasis mine.
My good friend Dr. Kevin R. Henke is a scientist and also an atheistic evolutionist. I had a lot of discussions with Kevin over religious views. I remember going over John 7:17 with him one day. It says:
John 7:17 (Amplified Bible)
17If any man desires to do His will (God’s pleasure), he will know (have the needed illumination to recognize, and can tell for himself) whether the teaching is from God or whether I am speaking from Myself and of My own accord and on My own authority.
I challenged Kevin to read a chapter a day of the Book of John and pray to God and ask God, “Dear God, if you are there then reveal yourself to me, and I pledge to serve you the rest of my life.”
Kevin did that and he even wrote down the thoughts that came to his mind and sent it to me and these thoughts filled a notebook.
Kevin did not become a Christian, but I am still praying for him. I do respect Kevin because he is an honest man. Interestingly enough he told me that he was pro-life because the unborn baby has all the genetic code at the time of conception that they will have for the rest of their life. Below are some other comments by other scientists:
Dr. Hymie Gordon (Mayo Clinic): “By all criteria of modern molecular biology, life is present from the moment of conception.”
Dr. Micheline Matthews-Roth (Harvard University Medical School): “It is scientifically correct to say that an individual human life begins at conception.”
Dr. Alfred Bongioanni (University of Pennsylvania): “I have learned from my earliest medical education that human life begins at the time of conception.”
Dr. Jerome LeJeune, “the Father of Modern Genetics” (University of Descartes, Paris): “To accept the fact that after fertilization has taken place a new human has come into being is no longer a matter of taste or opinion . . . it is plain experimental evidence.”
Science Matters #2: Former supermodel Kathy Ireland tells Mike Huckabee about how she became pro-life after reading what the science books have to say.
Back on April 27, 2009 Fox News ran a story by Hollie McKay(“Supermodel Kathy Ireland Lashes Out Against Pro Choice,”) on Jill Ireland.
It’s no secret that the majority of Hollywood stars are strong advocates for a woman’s right to choose whether or not she wants to terminate a pregnancy, however former “Sports Illustrated” supermodel-turned-entrepreneur-turned-author Kathy Ireland has gone against the grain of the glitterati and spoken out against abortion.
“My entire life I was pro-choice — who was I to tell another woman what she could or couldn’t do with her body? But when I was 18, I became a Christian and I dove into the medical books, I dove into science,” Ireland told Tarts while promoting her insightful new book “Real Solutions for Busy Mom: Your Guide to Success and Sanity.”
“What I read was astounding and I learned that at the moment of conception a new life comes into being. The complete genetic blueprint is there, the DNA is determined, the blood type is determined, the sex is determined, the unique set of fingerprints that nobody has had or ever will have is already there.”
However Ireland admitted that she did everything she could to avoid becoming a believer in pro-life.
“I called Planned Parenthood and begged them to give me their best argument and all they could come up with that it is really just a clump of cells and if you get it early enough it doesn’t even look like a baby. Well, we’re all clumps of cells and the unborn does not look like a baby the same way the baby does not look like a teenager, a teenager does not look like a senior citizen. That unborn baby looks exactly the way human beings are supposed to look at that stage of development. It doesn’t suddenly become a human being at a certain point in time,” Ireland argued. “I’ve also asked leading scientists across our country to please show me some shred of evidence that the unborn is not a human being. I didn’t want to be pro-life, but this is not a woman’s rights issue but a human rights issue.”
What is the real problem that Dr. Lewis Wolpert has? Unlike others who have examined the evidence he just outright dismisses it.
For instance, in an email dated 6-25-14 I sent him this information about the accuracy of the Bible:
Dr. Wolpert, you want some evidence that indicates that the Bible is true? Here is a good place to start and that is taking a closer look at the archaeology of the Old Testament times. Is the Bible historically accurate? Here are some of the posts I have done in the past on the subject: 1. The Babylonian Chronicle, of Nebuchadnezzars Siege of Jerusalem, 2. Hezekiah’s Siloam Tunnel Inscription. 3. Taylor Prism (Sennacherib Hexagonal Prism), 4. Biblical Cities Attested Archaeologically. 5. The Discovery of the Hittites, 6.Shishak Smiting His Captives, 7. Moabite Stone, 8. Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III, 9A Verification of places in Gospel of John and Book of Acts., 9B Discovery of Ebla Tablets. 10. Cyrus Cylinder, 11. Puru “The lot of Yahali” 9th Century B.C.E., 12. The Uzziah Tablet Inscription, 13. The Pilate Inscription, 14. Caiaphas Ossuary, 14 B Pontius Pilate Part 2, 14c. Three greatest American Archaeologists moved to accept Bible’s accuracy through archaeology.,
I sent Dr. Wolpert a letter that included many scriptures from the Old Testament that showed that the prophets predicted the Jews would be brought back from all over the world to rebirth the country of Israel again.
Is this good evidence to show there is a God behind it all?
First, isn’t it worth noting that the Old Testament predicted that the Jews would regather from all over the world and form a new reborn nation of Israel. Second, it was also predicted that the nation of Israel would become a stumbling block to the whole world. Third, it was predicted that the Hebrew language would be used again as the Jews first language even though we know in 1948 that Hebrew at that time was a dead language!!!Fourth, it was predicted that the Jews would never again be removed from their land.
HAVE THESE NOT IN FACT HAPPENED? Yet in the article below Dr. Wolpert insists, ” God doesn’t exist. He hasn’t done anything in the last 2,000 years.”
_________________

Six Impossible Things Before Breakfast
Cell biologist Lewis Wolpert has recently attained a measure of notoriety with the British public, primarily through the publication of his book Six Impossible Things Before Breakfast: The Evolutionary Origins of Belief (Faber, 2006). He also participated in a recent public debate on the existence of God with Christian philosopher William Lane Craig. The debate was hosted by the well-known journalist John Humphrys, and reported by him in a major article for the Daily Telegraph.1
Professor Wolpert, who is a vice president of the British Humanist Association, admits, ‘I stopped believing in God when I was fifteen or sixteen because he didn’t give me what I asked for’2 but he has subsequently and repeatedly justified his atheism by asserting that, ‘There is absolutely no evidence for the existence of God.’3
Lewis Wolpert’s Presumption of Atheism and the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ Objection to Belief in God
Problems with the presumption of atheism
Relying on the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection is a risky gambit for the atheist. As philosopher William Rowe observes, ‘To fail to provide any arguments for the non-existence of God is … to virtually concede the debate to the person who at least gives some arguments, however weak, in behalf of the position that God exists.’4Arguing for atheism on the basis that there is insufficient evidence for belief in God (and that, in the absence of such evidence, the benefit of the doubt should be given to atheism rather than theism or agnosticism) is always vulnerable to the possibility that new evidence – or a better formulation and appreciation of old evidence – might turn up. Such atheism cannot afford to be dogmatic, for ‘even if the theist could not muster good arguments for God’s existence, atheism still would not be shown to be true.’5 As atheist philosopher Kai Nielsen admits: ‘To show that an argument is invalid or unsound is not to show that the conclusion of the argument is false.… All the proofs of God’s existence may fail, but it still may be the case that God exists.’6
According to Robert A. Harris, ‘a common sense look at the world, with all its beauty, apparent design, meaning, and vibrancy, would seem to predispose a neutral observer to presume that God exists unless good evidence for his non-existence could be brought to bear … The fact that materialists often struggle with this issue, working to explain away the design of the creation, for example, would seem to back up this claim.’7 Nevertheless, British humanist Richard Norman asserts that, ‘the onus is on those who believe in a god to provide reasons for that belief. If they cannot come up with good reasons, then we should reject the belief.’8It was another British philosopher, Antony Flew (who recently became a theist9), who most famously urged that the ‘onus of proof must lie upon the theist’,10 and that unless compelling reasons for God’s existence could be given there should be a ‘presumption of atheism’. However, by ‘atheism’ Flew meant merely ‘non-theism’ – a non-standard definition of ‘atheism’ that includes agnosticism but excludes atheism as commonly understood. The presumption of atheism is, therefore, not particularly interesting unless (as with Richard Norman explicitly and Lewis Wolpert implicitly) it really is the presumption of atheism rather than the presumption of agnosticism. However, the former is far harder to defend than the latter. Paul Copan writes:
the ‘presumption of atheism’ demonstrates a rigging of the rules of philosophical debate in order to play into the hands of the atheist, who himself makes a truth claim. Alvin Plantinga correctly argues that the atheist does not treat the statements ‘God exists’ and ‘God does not exist’ in the same manner. The atheist assumes that if one has no evidence for God’s existence, then one is obligated to believe that God does not exist – whether or not one has evidence against God’s existence. What the atheist fails to see is that atheism is just as much a claim to know something (‘God does not exist’) as theism (‘God exists’). Therefore, the atheist’s denial of God’s existence needs just as much substantiation as does the theist’s claim; the atheist must give plausible reasons for rejecting God’s existence … in the absence of evidence for God’s existence, agnosticism, not atheism, is the logical presumption. Even if arguments for God’s existence do not persuade, atheism should not be presumed because atheism is not neutral; pure agnosticism is. Atheism is justified only if there is sufficient evidence against God’s existence.11
As Scott Shalkowski writes: ‘suffice it to say that if there were no evidence at all for belief in God, this would [at best] legitimize merely agnosticism unless there is evidence against the existence of God.’12 Steven Lovell similarly points out that, to avoid a double standard, the atheist cannot use the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ argument alone, but must combine it with one or more of the other objections to belief:
Time and again I’ve heard people say that they don’t believe in God because they think there is insufficient evidence for His existence. If the person saying this is an atheist (one who thinks that God doesn’t exist, that ‘God exists’ is a false statement), then they imply that they do have enough evidence for their atheism. Clearly, if we reject belief in God due to (alleged) insufficient evidence, then we would be irrational to accept atheism if the evidence for God’s non-existence were similarly insufficient. It would be a radical inconsistency. If theistic belief requires evidence, so must atheistic belief. If we have no evidence either way, then the logical conclusion would be agnosticism.13
There are, then, a number of serious problems with Wolpert’s use of the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ claim to justify a default ‘presumption of atheism’.
A popular objection to Theism
Despite these problems, the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection to theism is widely used by contemporary atheists. A 1998 survey of 1,700 American skeptics conducted by Skeptics Society director Michael Shermer and MIT social scientist Frank Sulloway showed that 37.9% of non-theistic skeptics said they didn’t believe in God because there is no proof. The 2005 Dare to Engage Questionnaire, which surveyed nearly five hundred fifteen-to-eighteen-year-old students, found that among self-designated atheists (20% of respondents) who took the opportunity to give an explanation of their disbelief, the third most popular response (given by 13% of those giving a reason for their atheism) was that there is a pervasive lack of evidence for God.
The ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection can be traced back to Bertrand Russell. Asked what he would say if he found himself standing before God on the judgement day being asked, ‘Why didn’t you believe in me?,’ Russell replied: ‘I’d say, “Not enough evidence, God! Not enough evidence!”’ Richard Dawkins says that in the same situation: ‘I’d quote Bertrand Russell’.14 (There is an interesting difference inattitude on this point between Russell et al on the one hand, and H.L. Mencken on the other hand, who answered essentially the same question by saying: ‘If I do fetch up with the twelve apostles, I shall say, “Gentlemen, I was wrong.”’15 In this context we should not shy away from the fact that atheists may – and note that I say mayrather than will – fail to appreciate genuine evidence for theism due to non-rational factors. As Piers Benn acknowledges, ‘since some theistic religions teach that sin can impair our thinking, we risk begging the question against those religions if we assume that if we can see no good reason for believing them, then they are almost certainly false.’16)
According to Richard Dawkins’ latest book, The God Delusion,17 if one examines natural theology, ‘the arguments turn out to be spectacularly weak.’18 He actually goes so far as to say that: ‘there is no evidence in favour of the God Hypothesis.’19This is an astonishing claim for Dawkins to make, since he once defined biology as ‘the study of complicated things that give the appearance of having been designed for a purpose.’20 So, according to Dawkins himself, there is, at the very least, prima facie evidence for the God hypothesis. The Humanist Manifesto II, drafted by Paul Kurtz and Edwin H. Wilson, declares with more caution than Dawkins or Wolpert that: ‘We find insufficient evidence for belief in the existence of a supernatural … theism … is an unproven and outmoded faith.’21 (The term ‘outmoded’ here is a fine example of what C.S. Lewis called ‘chronological snobbery’.22) Taking a historical view on the same objection, Kai Nielsen states that:
Starting with the early Enlightenment figures, finding acute and more fully developed critiques in Hume and Kant, and carried through by their contemporary rational reconstructers (e.g., Mackie, and Martin), the various arguments for the existence of God have been so thoroughly refuted that few would try to defend them today and even those few who do, do so in increasingly attenuated forms.23
Professor Wolpert likewise praises David Hume’s scepticism, stating: ‘Hume is the only philosopher I take seriously.’24 However, such claims are surprisingly out of touch with the reality of contemporary practice in the philosophy of religion. What William Lane Craig calls ‘the obsolete, eighteenth century objections of Hume and Kant’25 have received substantial replies from contemporary philosophers.26 David Hume, in particular, is widely regarded as an over-rated thinker who inspires much unnecessary kow-towing.27 According to James F. Sennett and Douglas Groothuis: ‘Natural theology is alive and well in contemporary philosophy; the supposed Humean refutation of the enterprise is a myth whose exposure is long overdue.’28
Many contemporary philosophers give their endorsement to the project of natural theology, and while individual arguments for God may often be defended in more rigorously cautious terms than was the norm in medieval scholasticism, today’s natural theology can hardly be called ‘attenuated’ when philosophers like Robert C. Koons are prepared to say that, ‘the evidence for theism has never been so clear and so strong as it is now.’29
Questioning the demand for evidence
However, questioning the claim that there is insufficient evidence for God’s existence is not the only way of responding to Wolpert’s objection. Many philosophers question the assumption that it is necessarily irrational to believe in God in the absence of evidential justification. After all, there are plenty of other beliefs about reality that appear to be rational despite the complete absence of evidential justification (e.g. the belief that the world is not a computer simulation as in the film The Matrix). In addition, the demand for evidence can neither be fulfilledad infinitum (i.e. it is impossible to justify all our beliefs) nor can it be consistently applied to itself (what evidential justification is there for the belief that all beliefs must have evidential justification in order to be rational?).
Sam Harris is another prominent atheist who, like Wolpert, condemns theists for adhering to a belief without any evidential basis: ‘While believing strongly, without evidence, is considered a mark of madness or stupidity in any other area of our lives, faith in God still holds immense prestige in our society.’30 Harris makes two mistakes in the space of this sentence. On the one hand, few theists would concede Harris’s assumption that their belief in God is predicated upon an absence of evidence. On the other hand, evidence is not always necessary for rational belief. Contrary to Harris’s statement, believing strongly without evidence is, in fact, considered a mark of rationality and common sense in many areas of life. For example, seriously doubting that the universe is older than five minutes old would rightly be considered a mark of madness or stupidity by most people. But the belief that the universe is older than this, rather than having been created five minutes ago complete with every empirical appearance of greater age (a belief held by Harris), must by the very nature of the case be accepted without evidential support. Hence, ‘being rational’ and ‘having evidential support’ cannot be one and the same thing. It is all well and good to demand that people hold all their beliefs rationally (for example, we shouldn’t pick our beliefs at random and we shouldn’t hold them in the face of overwhelming counter-evidence), but there is little sense in demanding that people hold all their beliefs on the basis of evidence.
Harris writes that, ‘An atheist is simply a person who believes that [theists] should be obliged to present evidence for [God’s] existence.’31 But the demand for every belief to be justified with evidence is self-defeating (on the one hand, what is the evidence for this claim? On the other hand, how would one ever satisfy this demand?). This means that the basic ‘not enough evidence’ argument deployed by Dawkins, Harris, Wolpert and other atheists is unsound because it is built upon a false premise. As philosopher John O’Leary-Hawthorne points out, ‘The basic argument from no evidence relies on the idea that in order to rationally believe something we need evidence for it. But from the perspective of many philosophers, the latter claim represents a gross oversimplification.’32
For example, we often find ourselves with perceptual beliefs (e.g. ‘I see a tree’) not because we have argued our way to the belief in question, but simply because our cognitive faculties lead us to hold that belief. Then again, I simply rememberdrinking coffee with friends yesterday; I don’t argue my way to the conclusion that I had coffee with friends yesterday based upon the available evidence. Despite the fact that my memory has proven unreliable on some occasions (something I only know through memory), there is no need for me to obtain independent evidence as to whether or not I drank coffee with friends yesterday in order for my belief in this matter to be rational. The truthful nature of my memory in this matter is one of my ‘basic’ beliefs. Fundamental moral beliefs are likewise basic beliefs: ‘Somewhere in one’s moral reasoning one reaches a set of beliefs that are bearers of intrinsic value; they are not valued as a means to some other end or for some extrinsic reason. At this level one reaches one’s basic moral beliefs.’33 ‘A whole host of other kinds of beliefs are also typically basic. There are, for example, elementary truths of logic… There are certain mathematical beliefs. And there are certain framework or fundamental beliefs such as belief in an external world, belief in the self, etc. These are foundational beliefs that we typically reason from and not to’.34 Indeed, the existence of some basic beliefs in our web of beliefs is an epistemic necessity, for as Roy Clouser points out:
it is impossible that the only beliefs we have the right to be certain about are the ones that we have proven … First, if everything needed to be proven, then the premises of every proof would also need to be proven. But if you need to prove the premises of every proof, you would then need a proof for your proof, and a proof for the proof of your proof, and so on – forever. Thus it makes no sense to demand that everything be proven because an infinite regress of proofs is impossible. So when the premises of an argument are themselves in need of proof, the series of arguments needed to prove its premises must eventually end with an argument whose premises are all ‘basic’, that is, not in need of proof … not all beliefs need proof, and proving anything depends on having beliefs that don’t need it … A second reason why not every belief needs proof is that the rules for drawing inferences correctly, the truths of logic and mathematics, cannot themselves have proofs because they are the very rules we must use in order to prove anything. If we were to use them to construct proofs of themselves, the proofs would already be assuming the truth of the very rules we were trying to prove! So proofs need belief in unproven rules as well as premises that we can know without proof.35
Without rejecting the claim that there are good arguments for belief in God, it can be cogently argued that belief in God can be rational without being based upon arguments for his existence. As Alan G. Padgett writes, ‘belief in God can be and often is perfectly legitimate and proper without any philosophical arguments. In other words, Christian faith does not depend upon the practice of philosophy (specifically natural theology) but rather upon more direct, immediate, and spiritual sources of the knowledge of God.’36 Such ‘properly basic’ belief in God is not a matter of ‘blind faith’, since it is not the result of simply picking a belief out of the air and since it remains sensitive to the need to defend belief against evidential challenges.
William Lane Craig attempted to point out this defect in the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ argument to Professor Wolpert before their recent debate on the existence of God in London, but without success.
Craig versus Wolpert – a mini-debate from Radio 4
In a mini debate between William Lane Craig and Lewis Wolpert held on BBC Radio 4 prior to their lengthier public encounter on the subject of God’s existence, Wolpert simply failed to understand Craig’s philosophical points about the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection. Having said that he thinks there is evidence for God (Craig mentions the Kalam cosmological argument, the moral argument and the fine tuning design argument), Craig challenged Wolpert’s assumption that one must have evidence for God in order to rationally believe in God. Craig points to the existence of these ‘properly basic beliefs’ which are rational to hold but which are not justified on the basis of other beliefs. Despite Craig explaining, with the use of several analogies, that without properly basic beliefs humans could not rationally believe anything (because we would have to have an infinite regress of evidence for all our beliefs), Wolpert revealed that he just didn’t get the point by simply repeating the same ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection.
Far from incidentally, the same point about infinite regress and explanation came into play when Craig answered Wolpert’s use of the ‘Who designed the designer?’ objection to the design argument (an objection beloved by Richard Dawkins in The God Delusion). Craig pointed out that for an explanation of some set of data to be rational, one need not have an explanation of the explanation. If one did need one, explanation would be impossible because to explain anything would invoke an infinite regress, in which case science would be impossible. Hence Wolpert’s use of the ‘explain that explanation’ demand is rather ironic!
Philosopher Tom Price has provided a concise summary of the public debate between Craig and Wolpert following their Radio 4 encounter, a debate which showed Wolpert failing to learn the lesson of his mini-debate with Craig:
Craig: God exists, here is the evidence.
Wolpert: God doesn’t exist, there is no evidence.
Craig: God exists, here is the evidence.
Wolpert: God doesn’t exist, who made God?
Craig: God does exist, he is an uncaused eternal being. Here is the evidence.
Wolpert: God doesn’t exist. He hasn’t done anything in the last 2,000 years.
Craig: That’s chronological snobbery. You don’t tell the time with an argument; you don’t tell if an argument is true or false, or if evidence is good or bad with a watch.
Wolpert: God doesn’t exist. We believe because we have a notion of cause and effect. This leads to toolmaking, and also to belief in God.
Craig: That’s the genetic fallacy. To confuse the origin of a belief with its truth or falsity. You need to deal with the arguments and evidence that I have presented.
Wolpert: God doesn’t exist. There is no evidence. Who made God?
Craig: Here is the evidence. God is an uncaused being. God does exist.
Wolpert: God doesn’t exist. There is no evidence.
Craig: God does exist. Here is the evidence.37
Or, as John Humphrys, who chaired the debate, reports:
You might assume that a debate between someone like Craig and someone like Wolpert – a Jew who lost his faith when he was 15 – would produce a riveting intellectual knockabout at least, and a profound discussion of whether God is delusion or reality at best. Sadly it didn’t work out like that. They might as well have been talking in different languages.
Here’s the essence of Craig’s case:
- God created the universe. The proof lies in the premise that whatever begins to exist has a cause. The universe began to exist; therefore it has a cause. It was brought into existence by something which is greater than (and beyond) it. And that something was a ‘personal being’.
- God ‘fine tunes’ the universe … There is no other logical explanation for the way things operate.
- Without God there can be no set of [objective] moral values.
- The ‘historical facts’ of the life of Jesus prove the basis for Christianity.
- God can be known and experienced [in a properly basic manner].
And here’s the essence of Wolpert’s rebuttal: its all bunkum. Every bit of it.38
Wolpert’s defence of atheism consisted of a few irrelevant, invalid arguments against the rationality of belief in God’s existence on the one hand (instances of chronological snobbery and the genetic fallacy respectively) and a total failure to interact with the purported evidence for God on the other hand – apparently on the grounds ‘that there is no evidence’ with which to interact! Given Craig’s use of theKalam cosmological argument, it is interesting to note that Wolpert candidly admits he has no alternative explanation for the Big Bang: ‘And then, of course, there’s the whole problem of where the universe itself came from. And that is a great mystery. Big bang, big schmang! How did that all happen? I haven’t got a clue.’39 How can someone who makes such repeated use of the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection fail so totally to even ‘deal with the argument and evidence’ presented by Craig? The answer to this question recently became clear in an interview between Wolpert and another Christian philosopher.
Wolpert’s question-begging obscurantism
In the hands of Lewis Wolpert, the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection is not at all what it seems. Wolpert says that atheism is justified because: ‘There is absolutely no evidence for the existence of God.’40 However, this assertion amounts to a magician-worthy piece of misdirection, a philosophical sleight-of-hand. Professor Keith Ward of Oxford University had the following revealing exchange with Wolpert concerning his ‘Insufficient Evidence’ justification in the course of an interview for the March 2007 edition of Third Way magazine:
Ward: What sort of evidence would count for you? Would it have to be scientific evidence of some sort?
Wolpert: Well, no… I think I read somewhere: If he turned the pond on Hamstead Heath into good champagne, it would be quite impressive.
Ward: A miracle would be sufficient?
Wolpert: But then you have to remember what David Hume said, that you wouldn’t believe in a reported miracle unless ‘the falsehood of [the] testimony would be more miraculous than the event which [it] relates.’
Ward: It’s one of his worst arguments, in my view.
Wolpert: Hume is the only philosopher I take seriously. I’m big against philosophy.41
Wolpert justifies his atheism by complaining that there is no evidence for the existence of God. So what sort of evidence would he accept? Would he accept scientific evidence? On Humean grounds (grounds that are widely accepted by contemporary philosophers to be defunct), he would not. Later in the same interview Ward asked Wolpert whether (in principle) there could be evidence of providence in history? Wolpert replied that there ‘absolutely [could] not’42 be any such evidence. Wolpert seems to include the evidence of religious experience among purported scientific evidence for God, because having provided a standard explanation of such experience in terms of evolutionary psychology (and despite admitting ‘I don’t have a good explanation, to be quite honest’43 for why he himself has escaped the evolutionary pressure to believe), Wolpert feels that he can dismiss all such experiences as delusional (an unsurprising move for someone who is a self-confessed ‘reductionist and a materialist’44). If Wolpert rules out scientific evidence for theism, will he accept philosophical evidence? He will not, because he is ‘big against philosophy’ (although he will embrace a double standard in order to allow Hume into the fold, to shore it up against scientific evidence for deity).
Having excluded a priori the very possibility of there being any evidence for God, it is perhaps unsurprising that Wolpert can find none. Nor is it surprising that he would fail to engage with purported evidence for God offered to him by Professor Craig. What is surprising is that having excluded a priori the possibility of there being any evidence for God, Wolpert should shirk the task of showing why Craig’s evidence is insufficient (where exactly do Craig’s arguments for God go wrong? Do they have false premises? Do they have invalid logic? Wolpert does not say) whilst continuing to justify his atheism primarily by repeating that ‘the evidence for God is not very good from my point of view.’45
Wolpert’s complaint is ultimately not that there is insufficient evidence for theism. Rather it is that since the possibility of there being sound evidence for theism would require materialism to be false, and since materialism is true, there can’t possibly be any sound evidence for theism. In other words Wolpert doesn’t merely think that there isn’t any evidence for God, he thinks that there can’t be any evidence for God. These are significantly different claims, and so it is not a trivial matter when Wolpert substitutes one for the other. There would be nothing wrong with taking this approach if Wolpert provided arguments purporting to show that materialism is true (or at least that theism is false), if he was prepared to enter into philosophical debate concerning the soundness of those arguments, and if he was prepared to extend the same courtesy to the theistic arguments of academics like Craig or Ward. Unfortunately Wolpert does not appear to be interested in fulfilling any of these conditions. He simply repeats the mantra that there is no evidence for God. Like doubting Thomas, Lewis Wolpert says ‘I will not believe unless I see’ – but unlike Thomas he keeps his eyes resolutely shut.
Wolpert and the Origin of Life
For example, during his interview with Keith Ward, Wolpert commented that:
How the cell came about is just… Wow! It’s absolutely mind-blowing. It’s truly miraculous – almost in a religious sense. I think we understand quite a lot about evolution – although even in later evolution there are problems for which we don’t have good explanations – but the origin of life itself, the origin of the cell itself, that’s not solved at all.46
Having heard such an interesting admission of scientific ignorance, Ward asked Wolpert whether he was happy to be described as a neo-Darwinian, and the following revealing exchange followed:
Wolpert: I’m afraid I would have to say that, yes.
Ward: So, even though you find it ‘miraculous’, you think we must account for the emergence of life purely in terms of random mutation and natural selection?
Wolpert: That’s the line we must pursue, yes.
Ward: Why ‘must’?
Wolpert: Because there really is no other way. Otherwise, you can only invoke God.47
In other words, Wolpert believes that the inherent capacities of the natural world (putting aside the cosmological question of why there is a natural world in the first place) must account for – and therefore must be capable of accounting for – both the origin and diverse nature of life on Earth. And this conclusion is philosophically deduced (not scientifically inferred) from the assumption that God could not possibly feature in the true account of these matters – presumably because Wolpert believes that there is no God. Once again Wolpert closes his eyes to the possibility of evidence pointing towards God’s existence by simply assuming that God does not exist! Once again, Wolpert’s use of the ‘Insufficient Evidence’ objection to belief in God is exposed as a rhetorical facade hiding a circular argument.
Conclusion
‘I am going to confront you with evidence before the Lord’ (1 Samuel 12:7).
Atheists, agnostics and theists alike should avoid Lewis Wolpert’s narrow-minded approach to the question of God’s existence, an approach that amounts to saying, ‘My mind is made up, don’t confuse me with the evidence.’ We all have our own personal default position on the subject of God’s existence, but we owe it to each other and to ourselves (and perhaps we even owe it to God) to take the alternatives seriously enough to decry blind faith.
Book title: Six Impossible Things Before Breakfast
Author: Lewis Wolpert
Keywords: Atheism, theism, evidence, proof, belief, rationality, God
Publisher: Faber and Faber
Pub. date (h/b): 16 March 2006
Pub. date (p/b): 4 January 2007
Recommended Resources
Paul Copan, ‘The Presumptuousness of Atheism’
William Lane Craig, ‘The Existence of God and the Beginning of the Universe’
William Lane Craig, ‘The Teleological Argument and the Anthropic Principle’
William Lane Craig, ‘Review: The Design Inference’
William Lane Craig, ‘The Indispensability of Theological Meta-Ethical Foundations for Morality’
William Lane Craig, ‘Contemporary Scholarship and the Historical Evidence for the Resurrection of Jesus Christ’
John Gray, ‘Myths of Meaning: Breaking the Spell and Six Impossible Things Before Breakfast’, New Statesman, 20 March 2006
John Humphrys, ‘The Return of God?’. Here is another eye-witness report of the Craig-Wolpert debate (The Peter Williams who has a comment on this page is not Peter S. Williams, the author of this article!)
Duncan McMillan, ‘Origins of Belief [a review of Six Impossible Things Before Breakfast]’
Keith Ward and Lewis Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, Third Way, March 2007
Peter S. Williams, ‘What do you believe is true even though you cannot prove it? – Comparing Dawkins’ faith with Flew’s evidence
Peter S. Williams, ‘A Change of Mind for Antony Flew’
Peter S. Williams, ‘Design and the Humean Touchstone’
Peter S. Williams, ‘An Introduction to Intelligent Design Theory’
R. Douglas Geivett and Gary R. Habermas (eds.), In Defence of Miracles, (Apollos, 1997)
James F. Sennett and Douglas Groothuis (eds.), In Defence of Natural Theology: A Post-Humean Assessment, (IVP, 2005)
References
[1] John Humphrys, ‘The Return of God?’.
[2] Lewis Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, Third Way, March 2007, p. 16.
[3] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 17.
[4] William Rowe ‘Reflections on the Craig-Flew Debate’ in Stan W. Wallace (ed.),Does God Exist? The Craig-Flew Debate, (London: Ashgate, 2003) pp. 70–71.
[5] Paul Copan, ‘The Presumptuousness of Atheism’.
[6] Kai Nielsen, Reason and Practice, (New York: Harper and Row, 1971) pp. 143–44.
[7] Robert A. Harris, The Integration of Faith and Learning: A Worldview Approach, (Eugene: Cascade, 2004) p. 83.
[8] Richard Norman, On Humanism, (Routledge, 2004) p. 16.
[9] cf. Peter S. Williams, ‘A Change of Mind for Antony Flew’.
[10] Antony Flew, The Presumption of Atheism, (London: Pemberton, 1976) p. 14.
[11] Copan, ‘The Presumptuousness of Atheism’.
[12] Scott A. Shalkowski, ‘Atheological Apologetics’ in R. Douglas Geivett and Brendan Sweetman (eds.), Contemporary Perspectives on Religious Epistemology, (Oxford, 1992) p. 63.
[13] Steven Lovell, ‘Evidence and Atheism’ (apparently no longer online).
[14] Richard Dawkins, ‘Richard Dawkins: You Ask The Questions Special’, The Independent, 5 December 2006.
[15] H.L. Mencken, quoted by Alistair Cooke.
[16] Piers Benn, ‘Is Atheism A Faith Position?’, Think, 13, summer 2006, p. 27.
[17] On The God Delusion, cf: Terry Eagleton, ‘Lunging, Flailing, Mispunching’,London Review of Books Vol. 28 No. 20, 19 October 2006; Jim Holt, ‘Beyond Belief’, New York Times 22 October 2006;
Alister E. McGrath, ‘The Dawkins Delusion’ and ‘Is God a Delusion? Atheism and the Meaning of Life’;
Thomas Nagel, ‘The Fear of Religion’, New Republic, 23 October 2006; H. Allen Orr, ‘A Mission to Convert’, New York Review of Books; Alvin Plantinga, ‘The Dawkins Confusion’; Richard Swinburne, ‘Response to Richard Dawkins’s Criticisms in The God Delusion‘; Peter S. Williams, ‘The Big Bad Wolf, Theism and the Foundations of Intelligent Design: A Review of Richard Dawkins’ The God Delusion‘; ‘Who’s Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf? Dawkins’ Failed Rebuttal of Natural Theology’; ‘Peter S. Williams Discusses The God Delusion‘; ‘The God DelusionDeconstructed – Southampton University’.
[18] Richard Dawkins, The God Delusion, (London: Bantam Press, 2006) p. 2.
[19] Dawkins, The God Delusion, p. 59.
[20] Richard Dawkins, The Blind Watchmaker, (Penguin, 1990) Preface, p. x.
[21] Paul Kurtz and Edwin H. Wilson, Humanist Manifesto II (1973) (my italics).
[22] cf. Art Lindsley, ‘C.S. Lewis on Chronological Snobbery’.
[23] Kai Nielsen, ‘Naturalistic explanations of theistic belief’, A Companion to the Philosophy of Religion, p. 403.
[24] Nielsen, ‘Naturalistic explanations of theistic belief’.
[25] William Lane Craig, ‘The Evidence for Christianity’.
[26] On Kant, see Norman L. Geisler, Christian Apologetics, (Baker, 1976).
[27] cf: R. Douglas Geivett and Gary R. Habermas (eds.), In Defence of Miracles, (Apollos, 1997); James F. Sennett and Douglas Groothuis (eds.), In Defence of Natural Theology: A Post-Humean Assessment, (Downers Grove: IVP, 2005); Richard Swinburne, ‘The Argument from Design’ in R. Douglas Geivett and Brendan Sweetman (eds.), Contemporary Perspectives on Religious Epistemology, (Oxford University Press, 1992); Charles Taliaferro and Anders Hendrickson, ‘Hume’s Racism and His Case Against the Miraculous’, Philosophia Christi, Volume 4, Number 2, 2002; Peter S. Williams, ‘Design and the Humean Touchstone’.
[28] James F. Sennett & Douglas Groothuis, editors of In Defence of Natural Theology: A Post-Humean Assessment, (IVP, 2005) p. 15.
[29] Robert C. Koons, ‘Science and Theism: Concord, not Conflict’, in Paul Copan & Paul K. Moser (eds.), The Rationality of Theism, (London: Routledge, 2003) p. 73.
[30] Sam Harris, Letter to a Christian Nation, (Bantam, 2007) p. 67.
[31] Harris, Letter to a Christian Nation, p. 51.
[32] John O’Leary-Hawthorne, ‘Arguments for Atheism’ in Michael J. Murray (ed.),Reason for the Hope Within, (Eerdmans, 1999) p. 124.
[33] Kelly James Clark, Return to Reason, (Eerdmans, 1998) p. 130.
[34] Clark, Return to Reason, p. 129.
[35] Roy Clouser, Knowing with the heart, (IVP, 1999) pp. 68–71.
[36] Alan G. Padgett, ‘The Relationship Between Theology and Philosophy’, James K. Beilby (ed.), For Faith and Clarity, (Baker, 2006) p. 39.
[37] Tom Price, ‘Craig vs. Wolpert’.
[38] John Humphrys, ‘The Return of God?’.
[39] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 18.
[40] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 17.
[41] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 17.
[42] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 17.
[43] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 18.
[44] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 17.
[45] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 16.
[46] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 18.
[47] Wolpert, ‘The Hard Cell’, p. 18.
© 2007 Peter Williams
_______
Unbelievable? Is Luke’s Description of Quirinius Historically Inaccurate?
 In my recent appearance on Unbelievable? with Justin Brierley (airing Saturday, August 24th2013), I had the opportunity to speak with a skeptic who cited Luke’s description of Quirinius (Luke 2:1–3) as a historical contradiction. Luke wrote that Joseph and Mary returned to Bethlehem for a census and “this was the first census taken while Quirinius was governor of Syria.” The Jewish historian, Josephus, confirmed the existence of this governor, but placed Quirinius’ ruling term from AD 5 to AD 6. This period of time is too late, however, as Matthew wrote that Jesus was born during the reign of Herod the Great (who according to Josephus, died nine years prior to the governorship of Quirinius). The authority of Josephus seems to be at odds with the accuracy of the Gospel writers, and like the account related to the execution of John the Baptist, we are left to decide which account is accurate (and which is not). Once again, it’s time to apply the overarching principles of witness reliability:
In my recent appearance on Unbelievable? with Justin Brierley (airing Saturday, August 24th2013), I had the opportunity to speak with a skeptic who cited Luke’s description of Quirinius (Luke 2:1–3) as a historical contradiction. Luke wrote that Joseph and Mary returned to Bethlehem for a census and “this was the first census taken while Quirinius was governor of Syria.” The Jewish historian, Josephus, confirmed the existence of this governor, but placed Quirinius’ ruling term from AD 5 to AD 6. This period of time is too late, however, as Matthew wrote that Jesus was born during the reign of Herod the Great (who according to Josephus, died nine years prior to the governorship of Quirinius). The authority of Josephus seems to be at odds with the accuracy of the Gospel writers, and like the account related to the execution of John the Baptist, we are left to decide which account is accurate (and which is not). Once again, it’s time to apply the overarching principles of witness reliability:
Principle One: Make Sure the Witnesses Were Present in the First Place
Both Luke and Josephus are historians relying on the observations and testimony of others (See Luke’s introduction in Luke 1:1-4), but Luke (writing in the late 50’s AD) has access to witnesses and sources far closer to the event than does Josephus (writing in the late 70’s AD and in the early 90’s AD). There is good reason to believe Luke is relying heavily on the testimony of Mark and Peter, and Mark’s Gospel is the earliest narrative of these events (written within 20 years of John’s execution); the case for the early dating of Luke’s text is cumulative and compelling. Luke’s account was, therefore, available to the early Christian and non-Christian observers of the life of Jesus. Interestingly, archaeological discoveries in the nineteenth century seem to confirm Quirinius (or someone with the same name) was also proconsul of Syria and Cilicia from 11 BC to the death of Herod. Quirinius’s name has been discovered on a coin from this period of time (as cited by John McRay in Archaeology and the New Testament), and on the base of a statue erected in Pisidian Antioch (as cited by Sir William Ramsay, The Bearing of Recent Discovery on the Trustworthiness of the New Testament). Quirinius may actually have ruled Syria during two separate periods and have taken two separate censuses. This is consistent with Luke’s account. In Luke 2:2, Luke refers to the “first census taken while Quirinius was governor of Syria” (describing Quirinius’ rule as the governor’s procurator), and in Acts 5:37, Luke describes a second census taken most likely between 6-7AD (as described by Josephus) when Quirinius was the formal governor of the region. Both Josephus and Luke link this second census to an uprising under Judas of Galilee. Only Luke’s sources were present during the actual events; as a result, Luke’s description of two separate censuses is reasonable.
Principle Two: Try to Find Some Corroboration for the Claims of the Witnesses
Historical accounts (like accounts from cold-case homicide witnesses) can be verified in a variety of ways. Sometimes we use physical evidence external to the account (like archaeological discoveries) and sometimes we use the testimony of other witnesses. While early skeptics of Luke’s account in the Book of Acts argued Luke to be unreliable (given he was the only ancient source for many of the events he described), archaeological discoveries quickly exonerated Luke as a historian. Luke accurately described a number of ancient people and locations (i.e. Lysanias, Pontius Pilate, Sergius Paulus, Gallio, Iconium and the Politarchs). In addition, Luke included a correct description of two ways to gain Roman citizenship (Acts 22:28), an accurate explanation of provincial penal procedure (Acts 24:1-9), a true depiction of invoking one’s roman citizenship, including the legal formula, de quibus cognoscere volebam (Acts 25:18), and an accurate account of being in Roman custody and the conditions of being imprisoned at one’s own expense (Acts 28:16 and Acts 28:30-31). Archaeologist and former Lukan skeptic, Sir William Ramsey investigated the archaeological discoveries relevant to Luke’s account and wrote, “(There are) reasons for placing the author of Acts among the historians of the first rank” (from St. Paul the Traveller and the Roman Citizen).
Principle Three: Examine the Consistency and Accuracy of the Witnesses
Accuracy and consistency are additional important aspects of eyewitness reliability. If we’re going to use Josephus’ record to discredit Luke, we need to at least be fair about assessing Josephus’ methodology and accuracy. For many years, the “post-enlightenment” academic consensus related to Luke and Josephus favored Josephus’ version of events, but recent scholarship, focusing solely on the textual criticism of Josephus, has challenged the consensus. Theodor Zahn, W. Lodder, Friedrich Spitta, W. Weber and more recently, D. R. Schwartz and John H. Rhoads have highlighted specific detrimental practices employed by Josephus. These scholars have noted Josephus’ susceptibility to “mistaken duplications” and to reporting simultaneous events from different sources “as if they happened at different times” (Rhoads). In addition, Josephus’ accounts are sometimes less focused on chronological beginnings or endings than they are on narrative “usefulness”. Josephus was not consistent nor completely accurate in his historical record. While many supporters of the Josephan account will at least admit Josephus was susceptible to numerical error and mistaken dating, they insist Josephus did not err with the date of Quirinius’ census. To make matters worse, the earliest copy of any of Josephus’ work is separated from the original authorship by 1100 years; we can’t even be sure we have an accurate version of what Josephus originally wrote.
Principle Four: Examine the Presence of Bias on the Part of the Witnesses
Skeptics often claim we can’t trust the gospel authors because they were Christians and presented Jesus in a unfairly favorable manner. I’ve written about this in Cold Case Christianity and demonstrated the difference between a presuppositional bias and a conviction based on observation, but even if Luke was biased in some way, what advantage does his dating of the census give his account? Luke’s version of events was written much earlier than that of Josephus; an inaccuracy in Luke’s birth narrative would not serve his purpose in providing Theophilus and accurate and “orderly account,” but would instead expose Luke as a liar. The birth narrative was clearly present in the earliest versions of Matthew and Luke’s gospels, as the birth and infancy details are referenced by the first students of the Apostles, including Ignatius, Polycarp and Clement. Scholars have observed that Josephus was not without bias of his own. As a patron of the emperor (Vespasian), Josephus often displays a pro-Roman partiality (even though he claims to be resisting such bias).
In trying to evaluate which ancient historical account (Luke or Josephus) is accurate, I once again apply the four dimensional template I’ve just described. I know better than to disqualify a witness simply because he or she might be wrong about a particular detail, but in this instance, I see no reason to favor Josephus’ account over that of Luke, particularly after evaluating the two accounts for historical proximity, corroboration, consistency, accuracy and bias. Once again, scholars don’t discredit the entire record of Josephus simply because they recognize was wrong in a number of places. We ought to afford the Biblical gospel authors the same benefit of the doubt.
J. Warner Wallace is a Cold-Case Detective, a Christian Case Maker, and the author of Cold-Case Christianity
– See more at: http://coldcasechristianity.com/2013/unbelievable-is-lukes-description-of-quirinius-historically-inaccurate/#sthash.5GrJ1VeF.dpuf
Related posts:
FRANCIS SCHAEFFER ANALYZES ART AND CULTURE Part 35 Robert M. Pirsig (Feature on artist Kerry James Marshall)
_________________
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx


Comments
Reblogged this on Talmidimblogging.